Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa are great for non-trivial everyday personal assistive tasks. However, they are limited in providing accurate answers to complex questions, real-time information, handling turns, and user interruptions.
Get started! Activate your free Stream account today and start prototyping your own voice AI agent!
Try asking Siri about the best things to do with kids in a particular city or location. It won't provide an accurate answer because it can’t access web search tools. On devices supporting Apple Intelligence, asking the same question will be handed off to ChatGPT.
As in-app conversational app features, voice agents are here to solve these limitations.
The sections below will help you discover how to build AI voice agents and the best creation platforms. Although it is not required for this article, you can set up a local Node.js server and run our demo iOS/iPadOS voice agent in SwiftUI. After setting up your local Node server, you can also test the conversational agent for other platforms by following these step-by-step tutorials:
What Is an AI Voice Agent?
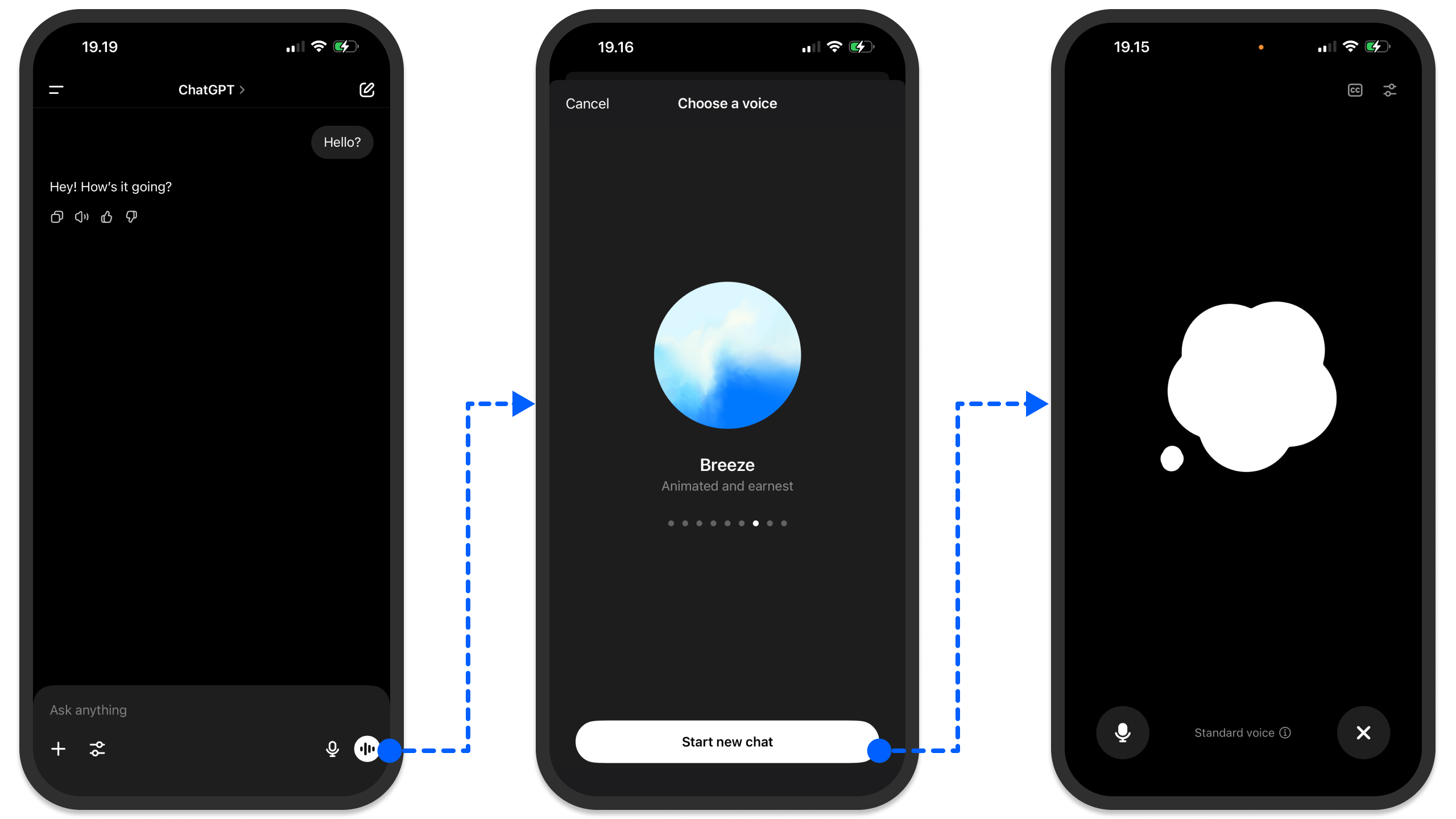
A voice agent is a conversational AI assistant capable of taking user instructions and responding with a human-like voice in real-time using a local or cloud-based LLM.
Like text-generation agents, voice-based ones use LLMs to output audio responses. The best way to think of it is to consider ChatGPT's voice mode, as illustrated in the above image. With the tap of a button and selecting your preferred voice, you can easily speak to ChatGPT for real-time responses.
In the following sections, we’ll look at the top platforms for building a ChatGPT-like voice mode experience.
Why Build a Voice Agent?
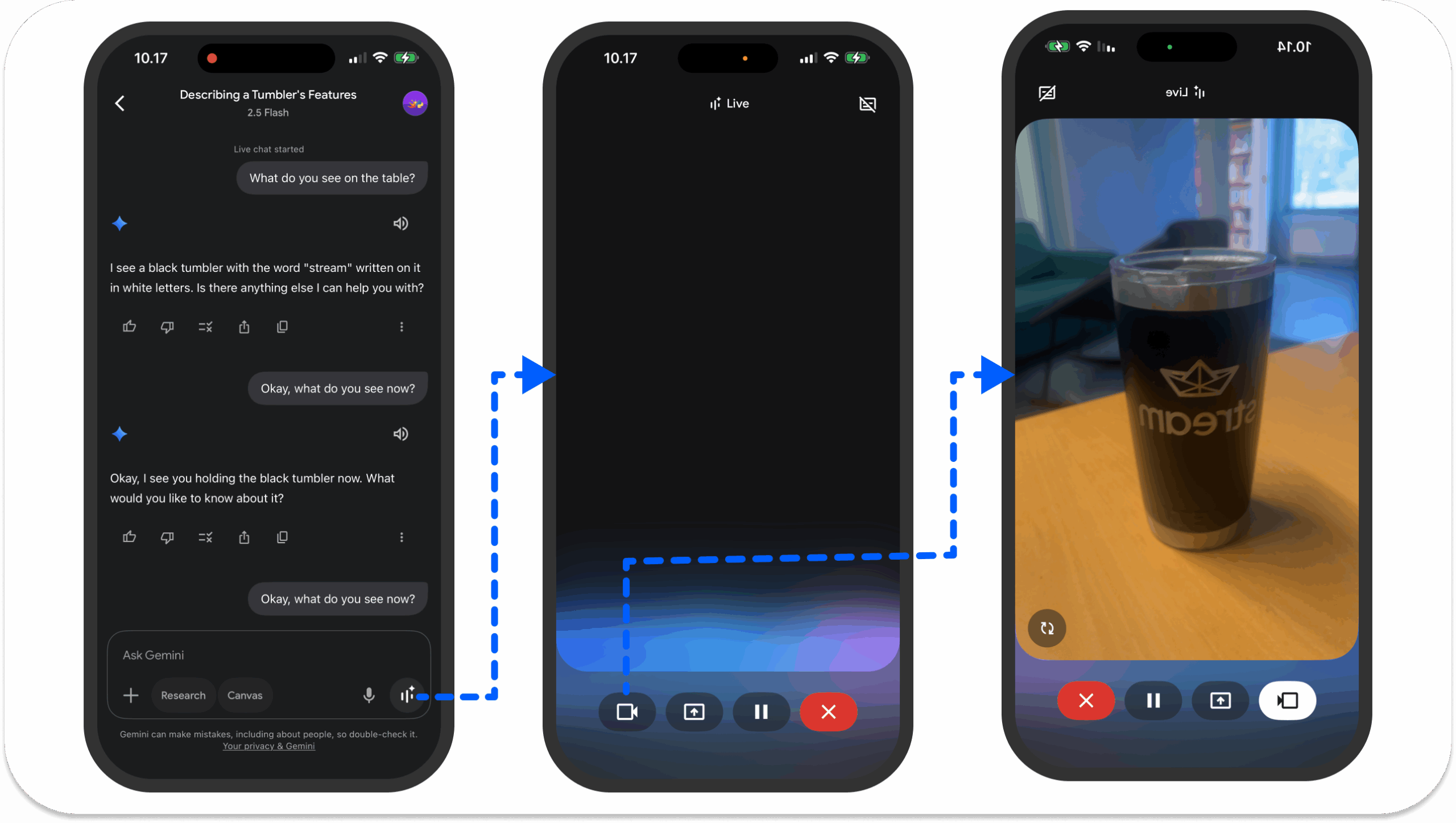
Like text-based AI agents, the support for MCP in voice applications helps agents retrieve accurate, real-time information from services such as Perplexity and Exa. With MCP, you can build an agent to manage tasks through Slack and Linear using voice interactions. You can also connect voice agents to MCP tools for custom workflows.
When creating your voice AI app, support for diverse accents may be needed. Luckily, major platforms, like the OpenAI Agents SDK, provide a library of voices to choose from. Voice-based agents can be used across many domains, including sales, marketing, customer support, small businesses, and enterprises.
- Video AI: An excellent use case of voice agents in a video AI setting is Gemini Live. It uses your phone's camera to see and understand objects around you and provide answers through speech interactions. Gemini Live also allows users to screen share their phone device's screen to ask questions about the content on the selected screen.
- Sales leads: Use a voice agent to follow up and contact potential customers for inbound sales in enterprises and small businesses.
- Customer support and call center: Voice agents can receive customer complaints and help fix issues.
- Personal assistant: Like Gemini Live, you can create a voice system to help you understand your surroundings and what you’re looking at. Another trending application area is computer and browser use. You can integrate a voice system with an AI browser agent to automate online booking and appointment scheduling.
- Social platform: Build voice agents to interact with people in social communities by giving real-time voice responses to users' queries.
- Gaming: Build character dialog and interactive narration systems with voice agents for online gaming platforms.
- Telecare: Use an AI voice to interact with patients and collect their information online in telehealth scenarios.
The Top 8 Platforms To Build Voice-Enabled Apps
Building a voice AI app can be daunting. Several aspects include backend infrastructure, audio quality, latency, and more. For these reasons, you can rely on frameworks, SDKs, and APIs to create AI solutions with voice as one of the main in-app features.
Most of these voice agent-building platforms offer a Python-first approach. TypeScript-based options are now catching up.
Let's look at the leading solutions and how to build quickly with them.
1. Stream Python AI SDK: Integrate In-App Voice AI
Stream allows developers to build real-time audio apps in React, Swift, Android, Flutter, JavaScript, and Python. With minimal effort, the recently released Python AI SDK helps developers create complex voice AI services, such as meeting assistants and bots for video conferencing.
You can use the Python SDK for transcribing, voice activity detection (VAD), converting speech to text, and vice versa. Aside from these features, you can integrate and extend your Stream-powered voice AI app with other leading platforms like:
The SDK's foundation is built with WebRTC and the OpenAI Real-Time API to endure low-latency communication.
Get Started with Stream Python AI SDK
Creating your first voice app with the Stream's Python AI SDK requires a few steps:
- Set up a Python environment and install the necessary dependencies. You can configure your Python virtual environment with this command.
python3 -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate
You may also set it up using uv and add a .env file to your project’s root directory and fill it up with the following:
1234STREAM_API_KEY=your-stream-api-key STREAM_API_SECRET=your-stream-api-secret STREAM_BASE_URL=https://pronto.getstream.io/ OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-your-openai-api-key
Sign up for a Stream dashboard account, create an app, and grab its API key and secret to substitute the above placeholders. With the STREAM_BASE_URL, you can create and join a Stream video call in your browser.
Next, run the following commands to install the Python AI SDK.
pip install --pre "getstream[plugins]"
# or using uv
uv add "getstream[plugins]" --prerelease=allow- Initialize a Stream client and user, and create a call.
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728from dotenv import load_dotenv from getstream import Stream from getstream.models import UserRequest from uuid import uuid4 import webbrowser from urllib.parse import urlencode # Load environment variables load_dotenv() # Initialize Stream client from ENV client = Stream.from_env() # Generates a new user ID and creates a new user user_id = f"user-{uuid4()}" client.upsert_users(UserRequest(id=user_id, name="My User")) # We can use this later to join the call user_token = client.create_token(user_id, expiration=3600) # Generate a user ID for the OpenAI bot that is added later bot_user_id = f"openai-realtime-speech-to-speech-bot-{uuid4()}" client.upsert_users(UserRequest(id=bot_user_id, name="OpenAI Realtime Speech to Speech Bot")) # Create a call with a new generated ID call_id = str(uuid4()) call = client.video.call("default", call_id) call.get_or_create(data={"created_by_id": bot_user_id})
- Create an OpenAI speech-to-speech pipeline.
The following code snippet allows you to create a speech-to-speech pipeline by initializing the OpenAIRealtime class of the SDK and launching the call with a web browser:
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031sts_bot = OpenAIRealtime( model="gpt-4o-realtime-preview", instructions="You are a friendly assistant; reply in a concise manner.", voice="alloy", ) try: # Connect OpenAI bot async with await sts_bot.connect(call, agent_user_id=bot_user_id) as connection: # Sends a message to OpenAI from the user side await sts_bot.send_user_message("Give a very short greeting to the user.") except Exception as e: # Handle exception finally: # Delete users when done client.delete_users([user_id, bot_user_id]) base_url = f"{os.getenv('EXAMPLE_BASE_URL')}/join/" # The token is the user token we generated from the client before. params = {"api_key": client.api_key, "token": user_token, "skip_lobby": "true"} url = f"{base_url}{call_id}?{urlencode(params)}" try: webbrowser.open(url) except Exception as e: print(f"Failed to open browser: {e}") print(f"Please manually open this URL: {url}")
When you put the code snippets together in the above steps and test out the combined code, you should see an output similar to this:
2. OpenAI: Create Voice Apps
OpenAI allows developers to integrate voice services with their apps in two ways. With its Python Agents SDK and TypeScript SDK, you can easily add voice agents to any AI application.
The SDK supports male and female TTSVoices such as Alloy, Ash, Coral, Echo, Fable, Onyx, Nova, Sage, and Shimmer. With its voice agent pipeline, you can transcribe an audio input into text, run a workflow for sequential text responses, and transform the text-based output into streaming audio.
Another way to build audio/speech experiences with OpenAI is to use its Realtime API. Using its WebRTC or WebSockets backend, developers can build multi-modal experiences supporting realtime text and speech generation, transcription, function calling, and more.
Some of the unique features of building voice agents with OpenAI include the following:
- Tools: Give your voice applications access to external services to execute actions.
- Agent monitoring: Provide guardrails and rules for voice agents to follow.
- Agent handoff: Create multiple agents who can assign tasks to others.
- Audio handling: It uses WebRTC to handle audio input/output by default.
- Session management: It allows configuring and customizing real-time sessions.
Get Started with OpenAI JS SDK
With the sample code below, you can start building voice apps with the OpenAI JS SDK. Check out voice agents quickstart to learn more.
1234567891011121314import { RealtimeAgent, RealtimeSession } from '@openai/agents/realtime'; const agent = new RealtimeAgent({ name: 'Assistant', instructions: 'You are a helpful assistant.', }); const session = new RealtimeSession(agent); // Automatically connects your microphone and audio output // in the browser via WebRTC. await session.connect({ apiKey: '<client-api-key>', });
3. ElevenLabs: Build Conversational Voice Agents
ElevenLabs is one of the leading platforms for building conversational AI applications. It provides developers and enterprises with all the building blocks for integrating low-latency voice agents with any service.
The example below demonstrates a realistic text-to-speech interaction.
With this platform, you can access categories of AI models for voice cloning, isolation, swapping, voice design, and making sound effects. Combinations of these models can be used to create and deploy interactive audio services.
For example, its latest model (Eleven V3) at the time of writing this article is an excellent choice for implementing realistic and expressive in-app text-to-speech. With its support for different categories of speech models, you have several options for video, audio, gaming, telehealth, and marketplace applications.
Get Started with ElevenLabs
ElevenLabs provides easy-to-use SDKs for Python and TypeScript developers. The sample code below is all you need to make your first API call to the Python voice AI SDK to create your text-to-speech app.
12345678910111213141516171819from dotenv import load_dotenv from elevenlabs.client import ElevenLabs from elevenlabs import play import os load_dotenv() elevenlabs = ElevenLabs( api_key=os.getenv("ELEVENLABS_API_KEY"), ) audio = elevenlabs.text_to_speech.convert( text="The first move is what sets everything in motion.", voice_id="JBFqnCBsd6RMkjVDRZzb", model_id="eleven_multilingual_v2", output_format="mp3_44100_128", ) play(audio)
Check out the developer quickstart to learn more about the TypeScript version of the SDK.
4. Deepgram: Build Voice AI Solutions
Deepgram is a voice AI application creation platform. Developers can use its API to build audio apps with text-to-speech, speech-to-speech, and speech-to-text models. To experience and see how Deepgram works, visit the URL above and try the interactive, real-time voice demo on the home page.
With Deepgram, you can try different models and APIs to build intelligent audio apps for use cases in customer service, telemedicine, sales, service ordering, etc. The quickest way to start building your app with Deepgram is to try its API playground.
Get Started with Deepgram
One advantage of using Deepgram is that its APIs are available for Python, JavaScript, C#, and Go. To build your first voice agent with any of the Deepgram SDKs, configure your environment and install the platform-specific SDK. The example commands below are for Python.
To begin with your preferred platform for implementing a voice agent, head to the Getting Started guides.
12345678mkdir deepgram-agent-demo cd deepgram-agent-demo touch index.py export DEEPGRAM_API_KEY="your_Deepgram_API_key_here" @TODO other Python commands # Install the SDK pip install deepgram-sdk
5. Vapi: Voice AI Agents For Developers

The Vapi platform helps developers build and deploy voice agents and AI products in Python, React, and TypeScript. It provides two ways to make intelligent voice apps. It's assistant's option allows you to create simple conversational services that may require a single system prompt for the underlying model's operations.
Example use cases of Vapi Assistants include simple question and answer systems and chatbots. If an agentic system has a complex logic or involves a multi-step process, you can use the workflow feature of Vapi to build your agents. Applications in this category are suitable for appointment scheduling and service ordering.
Vapi is an excellent choice for developers and enterprises developing voice AI products for call operations involving actual phone numbers. You can integrate it with several applications and model providers, such as Salesforce, Notion, Google Calendar, Slack, OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, and more.
- Multilingual support: The API supports multilingual operations. This means your app's users can speak to agents in English, Spanish, and 100+ other supported languages.
- External tools: Easily add external tools to allow your voice agent to perform accurate actions.
- Automated testing: Use simulated AI voices to create test suites for production-ready agents.
- Plugin any model: You can bring your favorite text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and speech-to-speech models from any major AI service provider.
Get Started with Vapi
Making your first voice AI app with Vapi or integrating it with an existing app is simple. The React sample code below can get you started.
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728import Vapi from "@vapi-ai/web"; import { useState, useEffect } from "react"; export const vapi = new Vapi("YOUR_PUBLIC_API_KEY"); // Get your public api key from the dashboard function VapiAssistant() { const [callStatus, setCallStatus] = useState("inactive"); const start = async () => { setCallStatus("loading"); const response = vapi.start("YOUR_ASSISTANT_ID"); // Get your assistant id from the dashboard }; const stop = () => { setCallStatus("loading"); vapi.stop(); }; useEffect(() => { vapi.on("call-start", () => setCallStatus("active")); vapi.on("call-end", () => setCallStatus('inactive')); return () => vapi.removeAllListeners(); }, []) return ( <div> {callStatus === "inactive" ? (<button onClick={start}>Start</button>) : null} {callStatus === "loading" ? <i>Loading...</i> : null} {callStatus === "active" ? (<button onClick={stop}>Stop</button>) : null} </div> ); }
Visit vapi.ai to try making voice agents for other platforms.
6. Play.ai: Build Real-Time Intelligent Voice Apps
PlayAI is a platform for making intelligent voice apps for the web and mobile. The platform allows engineers to create voice agents for healthcare, real estate, gaming, food delivery, EdTech, and more.
To see how the service works, check out the interactive voice chat demo from the above URL or try the PlayNote web app, which allows you to turn JPEG, PDF, EPUB, CSV, and several other files into a human-like-sounding audio format. Like other platforms, PlayAI has a library of AI voices for experimenting with your apps.
The PlayAI's playground/sandbox provides a starting point for experimenting, testing speech generation, and building audio experiences.
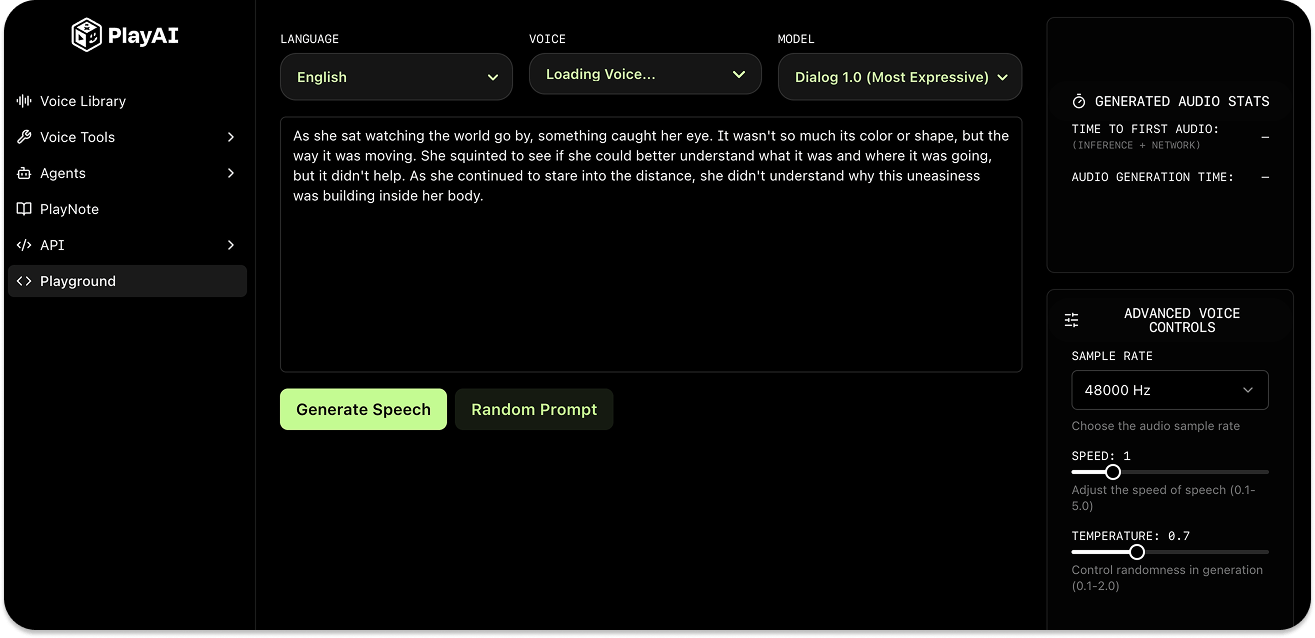
Get Started with PlayAI
You can use the PlayAI text-to-speech API in Bash, Python, JavaScript, Go, Dart, and Swift. First, set your API credentials on your machine.
12345678# macOS (zsh) echo 'export PLAYAI_KEY="your_api_key_here"' >> ~/.zshrc echo 'export PLAYAI_USER_ID="your_user_id_here"' >> ~/.zshrc source ~/.zshrc # Windows setx PLAYAI_KEY "your_api_key_here" setx PLAYAI_USER_ID "your_user_id_here"
Then, make your first API call to create an audio from a text prompt using this Curl script:
12345678910curl -X POST 'https://api.play.ai/api/v1/tts/stream' \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $PLAYAI_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -H "X-USER-ID: $PLAYAI_USER_ID" \ -d '{ "model": "PlayDialog", "text": "Hello! This is my first text-to-speech audio using PlayAI!", "voice": "s3://voice-cloning-zero-shot/baf1ef41-36b6-428c-9bdf-50ba54682bd8/original/manifest.json", "outputFormat": "wav" }' \
Running the above in your Terminal should output an audio file called hello.wav.
7. Pipecat: Build Voice AI Apps

Pipecat is one of the most widely used open-source frameworks for building conversational AI applications. The framework allows developers to create complex dialog systems, enterprise-grade customer support agents, multimodal interactions (video, voice, and images), and video meeting assistants.
Check out this X post to see a practical demo of Pipecat in action.
The client SDKs for Web, iOS, Android, and C++ allow you to build low-latency conversational apps with several AI services, tools, and underlying backend technologies such as WebRTC and WebSockets.
Get Started with Pipecat
You can start running Pipecat on a local machine by configuring your environment, installing the module, and switching to the cloud once your voice application is ready for production.
12345# Install the module pip install pipecat-ai # Set up your environment cp dot-env.template .env
Refer to the Pipecat’s GitHub repo for more code samples and detailed instructions on building conversational agents with the framework.
8. Cartesia: Create Realistic AI Voices
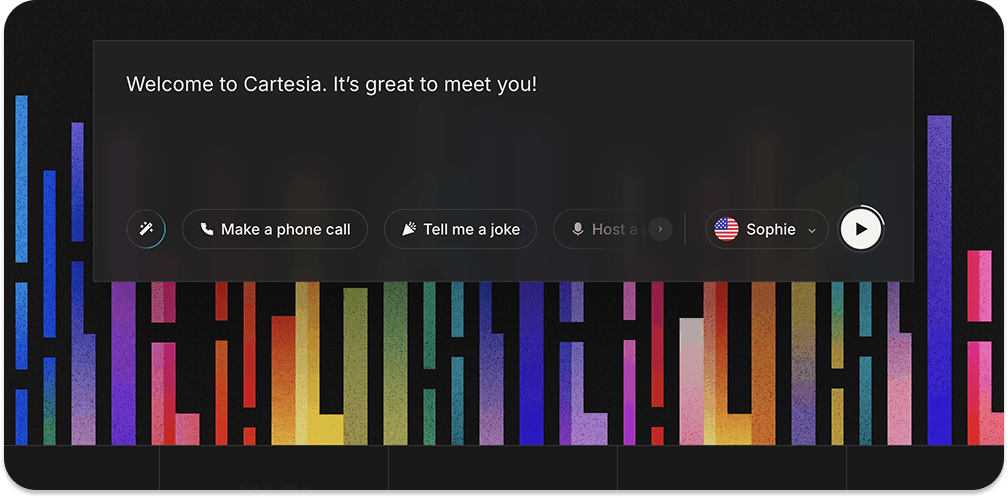
Cartesia is a developer-first platform for voice AI. The Cartesia API makes incorporating high-quality voices into any product easier. It also provides seamless support for extending voice agents with other platforms like LiveKit, Vapi, and Pipecat. You can build your speech applications in 15+ languages and deploy them anywhere and on any device.
To learn more about how Cartesia works, you can check out its Sonic text-to-speech and Ink-Whisper speech-to-text models.
Get Started with Cartesia
Depending on your machine, there are a few installation requirements for using the Cartesia API.
1234567891011# macOS brew install ffmpeg # Debian/Ubuntu sudo apt install ffmpeg # Fedora dnf install ffmpeg # Arch Linux sudo pacman -S ffmpeg
After you install any of the above for your computer, you can now make an API call to generate your first speech from text using cURL, Python, or JavaScript/TypeScript.
12345curl -N -X POST "https://api.cartesia.ai/tts/bytes" \ -H "Cartesia-Version: 2024-11-13" \ -H "X-API-Key: YOUR_API_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"transcript": "Welcome to Cartesia Sonic!", "model_id": "sonic-2", "voice": {"mode":"id", "id": "694f9389-aac1-45b6-b726-9d9369183238"}, "output_format":{"container":"wav", "encoding":"pcm_f32le", "sample_rate":44100}}' > sonic-2.wav
To go further, you can try Cartesia's Python and TypeScript SDKs.
Other Notable Voice AI Platforms
There are other excellent services like LiveKit, Kokoro TTS, and Moonshine for creating voice applications. You can also use platforms like Unmute.sh and OpenAI.fm to experiment and test with a library of natural and realistic AI voices.
To make voice apps for specific use cases, such as phone call operations, you can use services like Bland AI, Retell AI, and Synthflow AI. If you want to try open-source TTS models, check out Chatterbox TTS and the Speech Synthesis category on Hugging Face Spaces.
The Future of Voice Agents
This article covered eight of the best platforms you can use today to make speech AI products.
Although all the platforms covered in this article provide natural-sounding human-like voices, many have high latencies when interacting with agents. Some do not handle interruptions and noisy conditions properly. For example, many platforms will struggle to understand a user's voice, especially if a baby or a kid is playing and talking in the background.
As this AI field keeps improving regularly, future speech models, APIs, and SDKs will enhance their interruption capabilities, noise detection, and ensure low-latency speech-to-speech, speech-to-text, and text-to-speech interactions. Many of these platforms are currently closed source, but as the voice AI landscape evolves rapidly, open-source alternatives will continue to emerge.

