1panic: runtime error: invalid memory address or nil pointer dereference
If you ever used Go, you probably saw this error at least once. Somewhere a nil pointer or nil interface was passed to a function that doesn’t handle nil. In all cases this is a programming error, either the function should handle nil or the caller shouldn’t have passed nil to the function. This Go experience report will try to make the case that nil is often not needed and being forced to have nil-able pointers and interfaces can cause panics in production. We’ll also briefly discuss how Rust solves this issue and how their solution could be applied to Go.
Nil can be useful
Let’s first start off by showing why allowing a value to be nil can be useful. The main use case for nil is indicating that a value is “missing”. A good example of this is some code that parses JSON and needs to know if a field was provided or not. By using a pointer to an int you can differentiate between a missing key and a value that was 0:
12345678910111213package main import ( "encoding/json" "fmt" ) type Number struct { N int } type NilableNumber struct { N *int } func main() { zeroJSON := []byte(
But it has its downsides
However, even though nil can be a useful concept it has a lot of downsides as well. Tony Hoare, the inventor of "null references" even calls it his billion dollar mistake:
Null references were created in 1964 - how much have they cost? Less or more than a billion dollars? Whilst we don't know, the amount is probably in the order of an (American) billion - more than a tenth of a billion, less than ten billion.
Source: Tony Hoare - Null References: The Billion Dollar Mistake
The main problem in Go is that it is impossible to have a variable of a type which specifies that the variable is never missing, but still lets it be a pointer or interface.
Creating such a variable would be nice because pointers and interfaces obviously both have other use cases than encoding a missing value. Pointers allow modification of a variable in place and interfaces allow specifying an abstraction. Sometimes you require one of these use cases, but don’t want a missing value. Because there’s no way to encode this in the type system you are required to use a pointer or interface type which can be nil. This then causes a problem: How does a reader of code know if a variable is allowed to be nil or not?
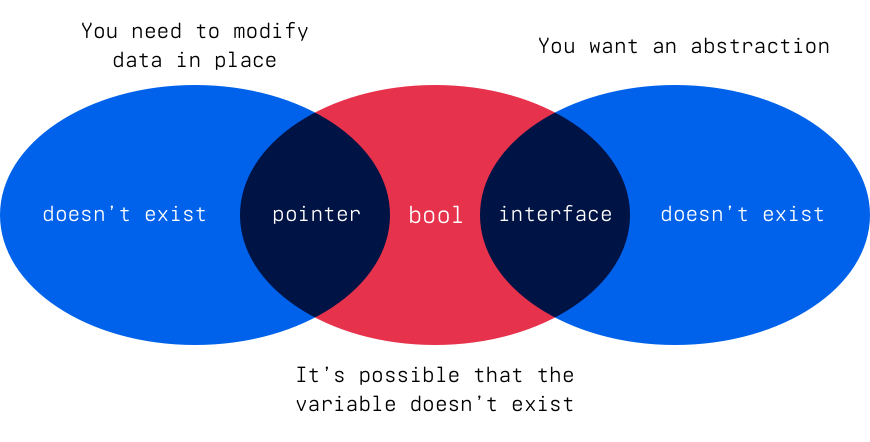
Finally, in all the cases where you don’t ever want the pointer or interface to be nil there’s also another problem. The zero value of the type is suddenly useless, because the only time when it would be the nil is when there’s a programmer error. This in turn makes it impossible to follow one of the Go proverbs:
Make the zero value useful.
Source: Rob Pike - Gopherfest - November 18, 2015
Examples of the problem
I’ve created the following small examples to show the problem in practice. It’s all example code where you don't ever want the type to be nil. For instance, when you create a function that accepts an interface you usually want to call the method(s) that the interface defines on the variable:
123456type Named interface { Name() string } func greeting(thing Named) string { return "Hello " + thing.Name() }
This code looks fine, but if you call greeting with nil the code compiles fine:
123func main() { greeting(nil) }
However, you will get our well known "nil pointer dereference" error at runtime:
1panic: runtime error: invalid memory address or nil pointer dereference
The same is true when using a pointer to a type that is used to modify a struct in-place. You expect to actually get an instance of the struct when writing a function like this:
123456type myNumber struct { n int } func plusOne(number *myNumber) { number.n++ }
But again when calling it with nil it will compile fine but error at runtime:
1234func main() { var number *myNumber plusOne(number) }
These two examples would be found easily during testing and code review. However, nil pointer dereferences are the cause for almost all panics we have in production. They usually happen in some rarely used codepath or because of unexpected inputs. To give a concrete example: We've had one panic where we wanted to log a recoverable error and have the log include a field of a field to a pointer of a struct. However, we forgot to check if the pointer wasn't nil before doing that. This caused an error that normally could be recovered from to escalate to a crash. In this case our code coverage also didn’t help, because the code was covered in the tests, just not with nil as an input.
Workarounds
One way to deal with this problem is by simply documenting that you should not pass nil to a function. A good example of this is the context package in the standard library of Go. It states the following in the documentation:
Do not pass a nil Context, even if a function permits it. Pass context.TODO if you are unsure about which Context to use.
Source: https://golang.org/pkg/context/
Obviously this is not really a robust solution though.
Another workaround might be to solve this problem with static analysis that warns you whenever you use a pointer or interface that has not been checked for nil before. Although in theory such a tool could be build, it currently does not exist. Furthermore I think it wouldn’t be desirable. Mainly because it would basically need to be an extension of the go type checker.
So far I've only found one solution that is actually robust. Which is to manually check that the value is not nil before actually using it. This needs to be done throughout all of your code and not just at the edge functions, which makes it easy to forget in some of the needed places. Apart from this it also brings another problem: if it is nil, what do you do? Usually you would want to return an error, but this can make the function signature more complicated even though it's just for the edge case where the function is used incorrectly.
123456func greeting(thing Named) (string, error) { if thing == nil { return "", errors.New("thing cannot be nil") } return "Hello " + thing.Name(), nil }
Solution?
To solve this problem changes to the language would be needed. I will not go into all of the possible solutions to this problem. Partly because experience reports are supposed to be mostly about the problem, but also since the best solution greatly depends on other features that are discussed for Go 2, such as generics and sum types.
I will show one possible solution though. I don’t think this is the best solution possible, but I would like to show it anyway because it can be implemented with minimal new language features and can be integrated into existing Go code step by step. However, it's only a solution for nil pointers, not nil interfaces. The idea is really simple and is also used by Rust and C++: add a pointer type that can never be nil. Below is some example code where I use the & character to define a non nil-able pointer, the plusOne function would now look like this:
123func plusOne(number &myNumber) { number.n++ }
You would then have the following behaviour
12345678910111213func TestNil() { var number *myNumber plusOne(number) // compile error: cannot use *myNumber as &myNumber, *myNumber can be nil } func TestPointer() { var number *myNumber = &myNumber{n: 5} plusOne(number) // compile error: cannot use *myNumber as &myNumber, *myNumber can be nil } func TestNonNilablePointer() { var number &myNumber = &myNumber{n: 5} plusOne(number) fmt.Println(number.n) // output: 6 }
And if you have a pointer you could use regular type casting to get a non nil-able pointer:
123456789101112func plusOnePointer(numberPointer *myNumber) error { if numberPointer == nil { return errors.New("number shouldn't be nil") } number := numberPointer.(*myNumber) plusOne(number) } func TestCastedPointer() { var number *myNumber = &myNumber{n: 5} plusOnePointer(number) // should handle error here fmt.Println(number.n) // output: 6 }
In case you are interested in how Rust solves this, this is what the previous code would look like in Rust. I think some other ideas from the Rust code below could be used to make the above Go solution even better, but like I said before that would require more changes:
https://gist.github.com/JelteF/917b6d233556e0de11de11b651490fb5
Conclusion
There are cases where you don't want a pointr or an interface ever to be nil. In these cases a check for nil is easily forgotten, which can lead to panics in production code. The workarounds are either not robust, or are hard to rigorously apply. Because of all this, it would be nice if Go would get language level support for pointers and interfaces that are never nil.
Some closing thoughts
There’s more types in Go that can be nil. Some types continue to work fine if they’re used normally when they are nil, such as slices and channels. Others, such as maps, will panic when used if they are nil, just like pointers and interfaces. Discussion for these types was kept out of this post, both to keep it shorter and because we haven’t come across a production crash because of using nil for these types. However, it’s probably good to keep these types in mind as well when designing a solution.
