const isMessageAIGenerated = (message) => !!message.ai_generated;
const App = ({ children }) => (
<Chat client={client} isMessageAIGenerated={isMessageAIGenerated}>
{children}
</Chat>
);SDK Integration
AI components work with the React Chat SDK out of the box.
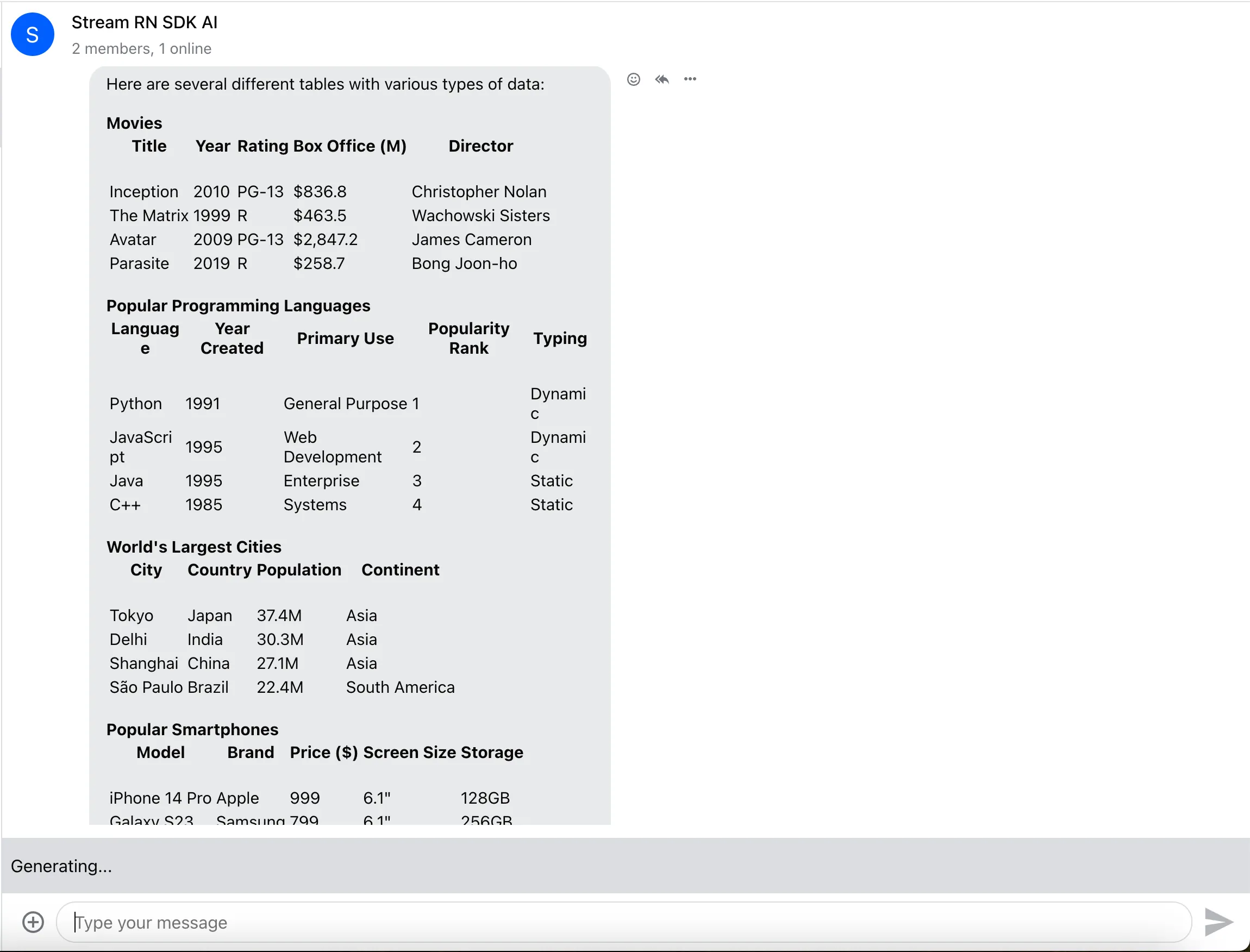
StreamedMessageText
StreamedMessageText ships with the SDK. It renders instead of MessageText when the isMessageAIGenerated function marks a message as AI-generated.
It displays the message with a typewriter animation and handles streaming updates for you.
Override it via the StreamedMessageText prop on Channel.
Example usage
The example above renders StreamedMessageText for messages where ai_generated is true.
AIStateIndicator
AIStateIndicator isn’t rendered by default. Render it as a child of Channel. It shows when the AI state is one of:
AI_STATE_GENERATINGAI_STATE_THINKING
Best Practices
- Use
isMessageAIGeneratedto keep AI rendering consistent across the app. - Show
AIStateIndicatoronly for active generation states. - Provide a stop button to let users cancel long responses.
- Keep streaming message UI compatible with default message layout.
- Validate attachments and model inputs before submission.
Example usage
const isMessageAIGenerated = (message) => !!message.ai_generated;
const App = () => (
<Chat client={client} isMessageAIGenerated={isMessageAIGenerated}>
<Channel channel={channel}>
<MessageList />
<AIStateIndicator />
<MessageInput />
</Channel>
</Chat>
);This shows the indicator above MessageInput when the AI state matches one of the states above.
StopAIGenerationButton
StopAIGenerationButton lets users stop a response mid-stream. It renders instead of the SendMessage button when the AI state is:
AI_STATE_GENERATINGAI_STATE_THINKING
Override it via Channel’s StopAIGenerationButton prop.
If you want to prevent rendering of the component altogether you can set the StopAIGenerationButton to null.
StreamingMessage
Integrating StreamingMessage is straightforward. The SDK uses isMessageAIGenerated to determine when to render its internal streaming message. If you consider a message AI-generated when message.ai_generated === true, your factory function could look like this:
const isMessageAIGenerated = (message: LocalMessage) => !!message.ai_generated;Then, provide your custom streaming message:
import { StreamingMessage } from "@stream-io/chat-react-ai";
const CustomStreamingMessage = () => {
const { message } = useMessageContext();
return <StreamingMessage text={message.text ?? ""} />;
};
// ...
<Channel {...otherChannelProps} StreamedMessageText={CustomStreamingMessage} />;This renders messages using @stream-io/chat-react-ai’s StreamingMessage instead of the default implementation.
Because this component still renders inside MessageSimple, you’ll also see other UI (reactions, read status, etc.). If that doesn’t suit your needs, build a custom message component while keeping the default styles:
import {
type MessageUIComponentProps,
useMessageContext,
MessageSimple,
Attachment,
MessageErrorIcon,
Channel,
} from "stream-chat-react";
import { StreamingMessage } from "@stream-io/chat-react-ai";
const CustomMessage = (props: MessageUIComponentProps) => {
const { message, isMyMessage, handleAction } = useMessageContext();
const attachments = message.attachments ?? [];
const hasAttachments = attachments.length > 0;
const rootClassName = clsx(
"str-chat__message str-chat__message-simple",
`str-chat__message--${message.type}`,
`str-chat__message--${message.status}`,
{
"str-chat__message--me": isMyMessage(),
"str-chat__message--other": !isMyMessage(),
"str-chat__message--has-attachment": hasAttachments,
},
);
if (!isMessageAIGenerated(message)) return <MessageSimple {...props} />;
return (
<div className={rootClassName}>
<div className="str-chat__message-inner" data-testid="message-inner">
<div className="str-chat__message-bubble">
{hasAttachments && (
<Attachment
actionHandler={handleAction}
attachments={attachments}
/>
)}
<StreamingMessage text={message?.text || ""} />
<MessageErrorIcon />
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
// ...
<Channel {...otherChannelProps} Message={CustomMessage} />;AIMessageComposer
To use AIMessageComposer, wire it to the existing MessageComposer:
import {
useMessageComposer,
useChannelActionContext,
useAttachmentsForPreview,
} from "stream-chat-react";
import { AIMessageComposer } from "@stream-io/chat-react-ai";
const CustomMessageComposer = () => {
const composer = useMessageComposer();
const { sendMessage } = useChannelActionContext();
const { attachments } = useAttachmentsForPreview();
return (
<AIMessageComposer
onChange={(event) => {
const input = event.currentTarget.elements.namedItem(
"attachments",
) as HTMLInputElement | null;
const files = input?.files ?? null;
if (files) composer.attachmentManager.uploadFiles(files);
}}
onSubmit={async (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
const target = event.currentTarget;
const formData = new FormData(target);
const message = formData.get("message");
composer.textComposer.setText(message as string);
const composedData = await composer.compose();
if (!composedData) return;
target.reset();
composer.clear();
await sendMessage(composedData);
}}
>
<AIMessageComposer.AttachmentPreview>
{attachments.map((attachment) => (
<AIMessageComposer.AttachmentPreview.Item
key={attachment.localMetadata.id}
file={attachment.localMetadata.file}
state={attachment.localMetadata.uploadState}
imagePreviewSource={attachment.localMetadata.previewUri as string}
onDelete={() => {
composer.attachmentManager.removeAttachments([
attachment.localMetadata.id,
]);
}}
onRetry={() => {
composer.attachmentManager.uploadAttachment(attachment);
}}
/>
))}
</AIMessageComposer.AttachmentPreview>
<AIMessageComposer.TextInput />
<AIMessageComposer.FileInput />
<AIMessageComposer.SpeechToTextButton />
<AIMessageComposer.ModelSelect />
<AIMessageComposer.SubmitButton />
</AIMessageComposer>
);
};
//...
<MessageInput Input={CustomMessageComposer} />;You can pick and choose which input components to render, and wrap them to customize layout. The inputs are intentionally minimal with helpful defaults. TextInput, FileInput, and SpeechToTextButton manage internal state, which you can access via useText or useAttachments.