Localization
The Android SDK's Compose UI Components are available in multiple languages out-of-the-box. At the moment we support the following languages (and more will be added in the future):
English is used as the default language.
If your app doesn't support all these languages, you might want to remove some of them.
| English | Italian |
|---|---|
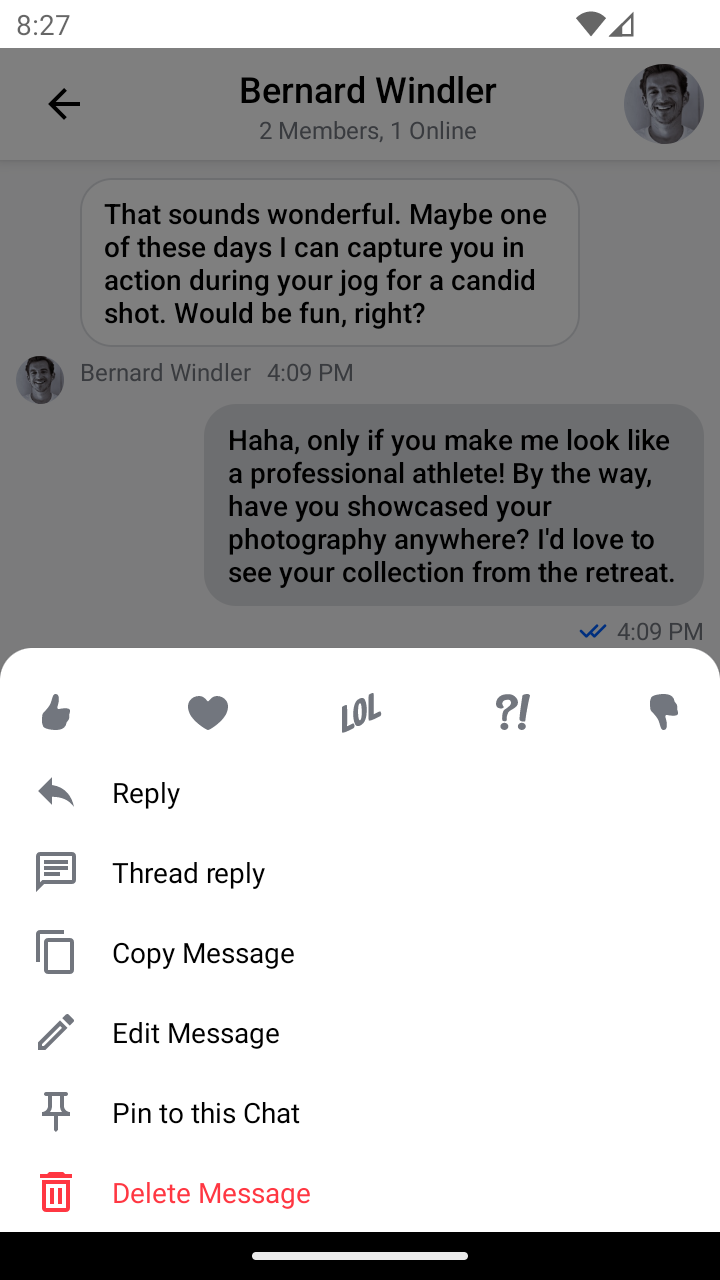 | 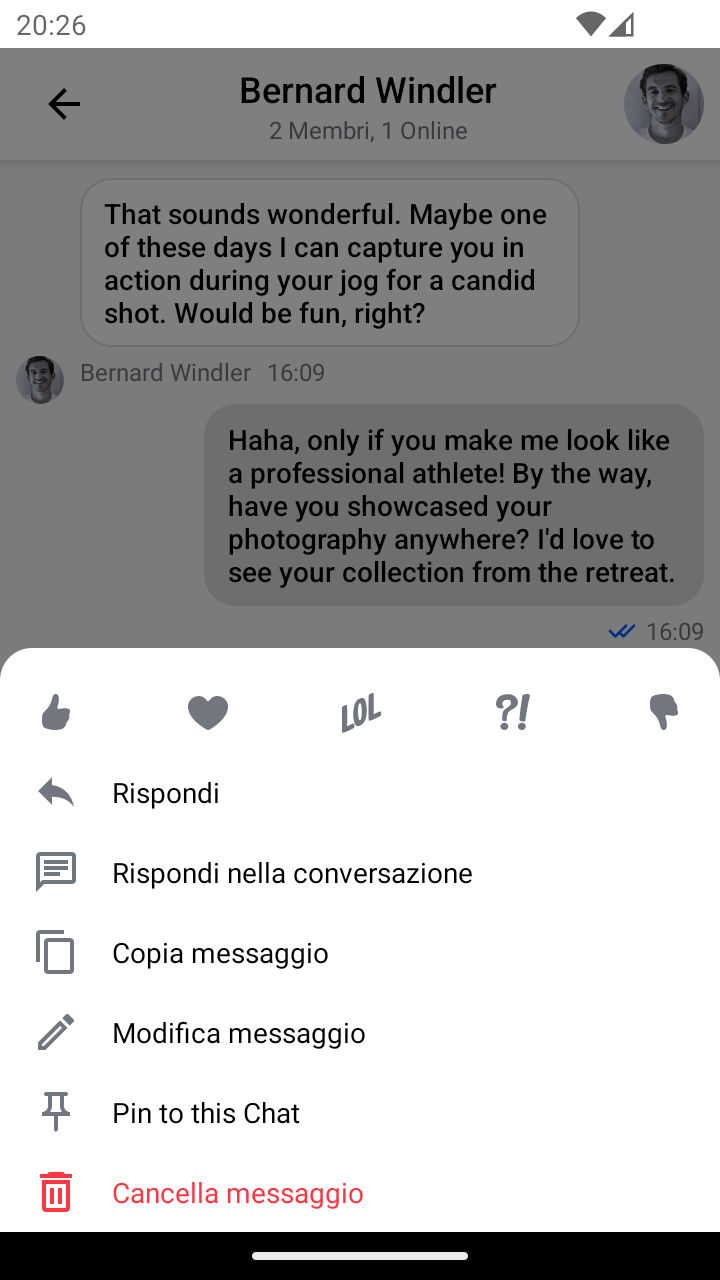 |
What is Localization?
If you deploy your app to users who speak another language, you might want to internationalize (localize) it. That means you need to write the app in a way that makes it possible to localize values like text and layouts for each language or locale that the app supports. For more information, see the official Android documentation.
Support for different languages in the SDK is based on the standard Android mechanism of switching resources on system locale change. The locale will be set automatically, based on system preferences. You can provide custom localization for the SDK's string resources by overriding them in the locale-specific /res/values directories of your project.
All of the string resources names provided by Stream SDK are prefixed with stream_compose_, for example:
<string name="stream_compose_message_list_empty_messages">No messages</string>
Adding a new language
Let's see how you can add support for additional languages in the SDK. As an example, we'll implement a custom Polish language translation for the ChannelListHeader UI component.
Usually, base string resources are located in the /res/values/strings.xml file. In order to add translations for the new language (PL) we are going to create a new strings.xml file under res/values-pl directory.
Let's take a look at the strings.xml file and discover strings defined for ChannelListHeader:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="stream_compose_disconnected">Disconnected</string>
<string name="stream_compose_waiting_for_network">Waiting for network</string>
</resources>
As you can see there are two string resources used by this UI component. Let's say we need to localize only the one called stream_compose_waiting_for_network.
In order to do that, we need to add the following string resource to the target locale-specific file. In our case, this will be the res/values-pl/strings.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="stream_compose_waiting_for_network">Oczekiwanie na połączenie</string>
</resources>
As the result, your app will display Oczekiwanie na połączenie text on devices set to a Polish locale.
Overriding existing languages
To override strings for a language supported by default, create new string resources in the locale-specific /res/values-XX directories of your project with the same resource name. Here you can find a list of available text resources.
Overriding the default language
To change the strings used by default, place the string resources you want to override inside the /res/values directory directory.
Removing existing languages
The Android UI Components include resources for all of the languages mentioned above. If your app doesn't support all those languages, you can exclude some of them by explicitly defining a list of supported languages inside your build.gradle file:
defaultConfig {
resConfigs "en", "es"
}
With the configuration here, your app will include only English and Spanish resources.
Automatic Translation
Stream Chat provides the ability to run users' messages through automatic translation. While machine translation is never perfect it can enable two users to communicate with each other without speaking the same language.
In order to enable automatic translation, the following steps are required to do in the Client SDKs:
Enabling the feature in the Compose SDK
ChatTheme(
autoTranslationEnabled = true,
) {
// ...
}
Supporting auto-translation in the custom message transformers
Please, take into account, that if you are using a custom MessagePreviewFormatter,
MessageTextFormatter, or QuotedMessageTextFormatter implementations you need to support the auto-translation feature by yourself.
The following example shows how to do that:
val getTranslatedText: (Message, User?) -> String = { message, currentUser ->
when (autoTranslationEnabled) {
true -> currentUser?.language?.let { message.getTranslation(it) } ?: message.text
else -> message.text
}
}
ChatTheme(
messagePreviewFormatter = object : MessagePreviewFormatter {
override fun formatMessagePreview(message: Message, currentUser: User?): AnnotatedString {
return buildAnnotatedString {
val translatedText = getTranslatedText(message, currentUser)
append(translatedText)
// add your custom styling here
}
}
},
messageTextFormatter = object : MessageTextFormatter {
override fun format(message: Message, currentUser: User?): AnnotatedString {
return buildAnnotatedString {
val translatedText = getTranslatedText(message, currentUser)
append(translatedText)
// Your custom styling here
}
}
},
quotedMessageTextFormatter = object : QuotedMessageTextFormatter {
override fun format(message: Message, replyMessage: Message?, currentUser: User?): AnnotatedString {
return buildAnnotatedString {
val translatedText = getTranslatedText(message, currentUser)
append(translatedText)
// Your custom styling here
}
}
}
) {
// Your UI content
}
Enabling the feature for Push Notifications
val notificationConfig = NotificationConfig(
//...
autoTranslationEnabled = true,
//...
)
val notificationHandler = NotificationHandlerFactory.createNotificationHandler(
//...
notificationConfig = notificationConfig,
//...
)
ChatClient.Builder(apiKey, context)
//...
.notifications(notificationConfig, notificationHandler)
//...
.build()
Providing the language when connecting the user
client.connectUser(user = User(id = "userId", language = "en"), token = "userToken").await()
For more information, see the full guide to adding automatic translation.