<io.getstream.chat.android.ui.message.composer.MessageComposerView
android:id="@+id/messageComposerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />Message Composer
MessageComposerView replaces MessageInputView, addressing most of its pain-points, including
extensibility, maintainability, etc. Just like the original view, the revamped component allows
users to participate in the chat by sending messages and attachments.

It supports the following features:
- Emoticons
- Attachments
- Slash Commands
- Typing events
- Editing messages
- Threads
- Mentions
- Replies
Let's see how to integrate the new MessageComposerView in your UI.
Usage
To use MessageComposerView, include it in your XML layout.
The recommended way of setting up MessageComposerView is by binding it to the MessageComposerViewModel. This will make it fully functional by setting up any necessary listeners and data handling.
// Create MessageComposerViewModel for a given channel
val factory = MessageListViewModelFactory(cid = "messaging:123")
val messageComposerViewModel: MessageComposerViewModel by viewModels { factory }
// Bind MessageComposerViewModel with MessageComposerView
messageComposerViewModel.bindView(messageComposerView, viewLifecycleOwner)// Create MessageComposerViewModel for a given channel
ViewModelProvider.Factory factory = new MessageListViewModelFactory.Builder()
.cid("messaging:123")
.build();
ViewModelProvider provider = new ViewModelProvider(this, factory);
MessageComposerViewModel viewModel = provider.get(MessageComposerViewModel.class);
// Bind MessageComposerViewModel with MessageComposerView
MessageComposerViewModelBinding.bind(viewModel, messageComposerView, getViewLifecycleOwner());Because it doesn't make sense to use the MessageComposerView as a standalone component, you also need to integrate it with the MessageListView:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<io.getstream.chat.android.ui.message.list.MessageListView
android:id="@+id/messageListView"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/messageComposerView"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<io.getstream.chat.android.ui.message.composer.MessageComposerView
android:id="@+id/messageComposerView"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>// Create ViewModels for MessageComposerView and MessageListView
val factory = MessageListViewModelFactory(cid = "messaging:123")
val messageComposerViewModel: MessageComposerViewModel by viewModels { factory }
val messageListViewModel: MessageListViewModel by viewModels { factory }
// Bind MessageComposerViewModel with MessageComposerView
messageComposerViewModel.bindView(messageComposerView, viewLifecycleOwner)
// Bind MessageListViewModel with MessageListView
messageListViewModel.bindView(messageListView, viewLifecycleOwner)
// Integrate MessageComposerView with MessageListView
messageListViewModel.mode.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { mode ->
when (mode) {
is MessageMode.MessageThread -> {
messageComposerViewModel.setMessageMode(MessageMode.MessageThread(mode.parentMessage))
}
is MessageMode.Normal -> {
messageComposerViewModel.leaveThread()
}
}
}
messageListView.setMessageReplyHandler { _, message ->
messageComposerViewModel.performMessageAction(Reply(message))
}
messageListView.setMessageEditHandler { message ->
messageComposerViewModel.performMessageAction(Edit(message))
}// Create ViewModels for MessageComposerView and MessageListView
ViewModelProvider.Factory factory = new MessageListViewModelFactory.Builder()
.cid("messaging:123")
.build();
ViewModelProvider provider = new ViewModelProvider(this, factory);
MessageComposerViewModel messageComposerViewModel = provider.get(MessageComposerViewModel.class);
MessageListViewModel messageListViewModel = provider.get(MessageListViewModel.class);
// Bind MessageComposerViewModel with MessageComposerView
MessageComposerViewModelBinding.bind(messageComposerViewModel, messageComposerView, getViewLifecycleOwner());
// Bind MessageListViewModel with MessageListView
MessageListViewModelBinding.bind(messageListViewModel, messageListView, getViewLifecycleOwner());
// Integrate MessageComposerView with MessageListView
messageListViewModel.getMode().observe(getViewLifecycleOwner(), mode -> {
if (mode instanceof MessageMode.MessageThread) {
messageComposerViewModel.setMessageMode(new MessageMode.MessageThread(((MessageMode.MessageThread) mode).getParentMessage()));
} else if (mode instanceof MessageMode.Normal) {
messageComposerViewModel.leaveThread();
}
});
messageListView.setMessageReplyHandler((cid, message) -> messageComposerViewModel.performMessageAction(new Reply(message)));
messageListView.setMessageEditHandler((message) -> messageComposerViewModel.performMessageAction(new Edit(message)));In the snippet above, you initialize the message composer and integrate it with the MessageListView by passing actions from the message list to the composer.
This will produce a fully working solution, as shown in the image below.
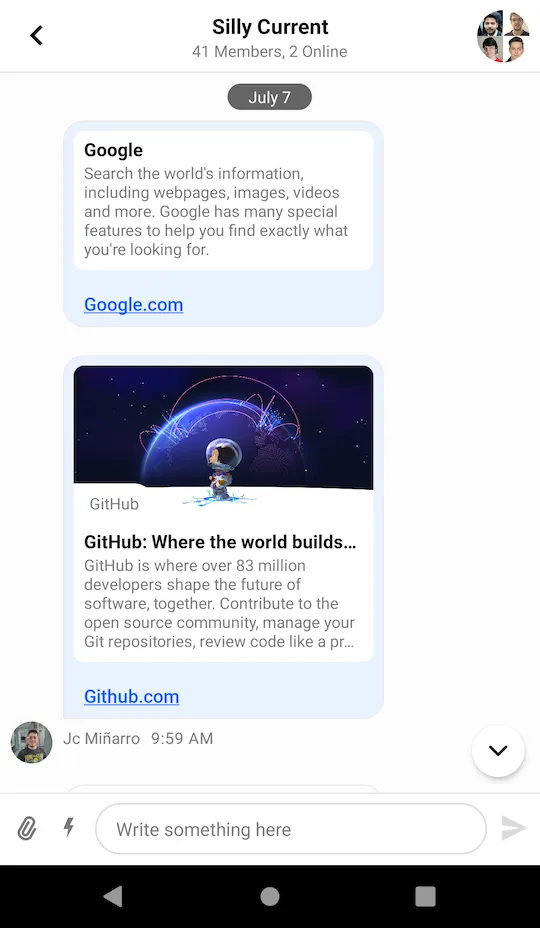
Handling Actions
To handle actions supported by the MessageComposerView you can set the corresponding listeners:
messageComposerView.sendMessageButtonClickListener = {
// Handle send button click
}
messageComposerView.textInputChangeListener = { text ->
// Handle input text change
}
messageComposerView.attachmentSelectionListener = { attachments ->
// Handle attachment selection
}
messageComposerView.attachmentRemovalListener = { attachment ->
// Handle attachment removal
}
messageComposerView.mentionSelectionListener = { user ->
// Handle mention selection
}
messageComposerView.commandSelectionListener = { command ->
// Handle command selection
}
messageComposerView.alsoSendToChannelSelectionListener = { checked ->
// Handle "also send to channel" checkbox selection
}
messageComposerView.dismissActionClickListener = {
// Handle dismiss action button click
}
messageComposerView.commandsButtonClickListener = {
// Handle commands button click
}
messageComposerView.dismissSuggestionsListener = {
// Handle when suggestions popup is dismissed
}
messageComposerView.attachmentsButtonClickListener = {
// Handle attachments button click
}messageComposerView.setSendMessageButtonClickListener(() -> {
// Handle send button click
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setTextInputChangeListener((text) -> {
// Handle input text change
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAttachmentSelectionListener((attachments) -> {
// Handle attachment selection
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAttachmentRemovalListener((attachment) -> {
// Handle attachment removal
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setMentionSelectionListener((user) -> {
// Handle mention selection
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setCommandSelectionListener((command) -> {
// Handle command selection
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAlsoSendToChannelSelectionListener((checked) -> {
// Handle "also send to channel" checkbox selection
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setDismissActionClickListener(() -> {
// Handle dismiss action button click
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setCommandsButtonClickListener(() -> {
// Handle commands button click
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setDismissSuggestionsListener(() -> {
// Handle when suggestions popup is dismissed
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAttachmentsButtonClickListener(() -> {
// Handle attachments button click
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});If you don't set your custom listeners, the default listeners from the MessageComposerViewModel::bindView method will be used:
messageComposerView.sendMessageButtonClickListener = {
messageComposerViewModel.sendMessage(messageComposerViewModel.buildNewMessage())
}
messageComposerView.textInputChangeListener = { text ->
messageComposerViewModel.setMessageInput(text)
}
messageComposerView.attachmentSelectionListener = { attachments ->
messageComposerViewModel.addSelectedAttachments(attachments)
}
messageComposerView.attachmentRemovalListener = { attachment ->
messageComposerViewModel.removeSelectedAttachment(attachment)
}
messageComposerView.mentionSelectionListener = { user ->
messageComposerViewModel.selectMention(user)
}
messageComposerView.commandSelectionListener = { command ->
messageComposerViewModel.selectCommand(command)
}
messageComposerView.alsoSendToChannelSelectionListener = { checked ->
messageComposerViewModel.setAlsoSendToChannel(checked)
}
messageComposerView.dismissActionClickListener = {
messageComposerViewModel.dismissMessageActions()
}
messageComposerView.commandsButtonClickListener = {
messageComposerViewModel.toggleCommandsVisibility()
}
messageComposerView.dismissSuggestionsListener = {
messageComposerViewModel.dismissSuggestionsPopup()
}messageComposerView.setSendMessageButtonClickListener(() -> {
messageComposerViewModel.sendMessage(messageComposerViewModel.buildNewMessage());
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setTextInputChangeListener((text) -> {
messageComposerViewModel.setMessageInput(text);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAttachmentSelectionListener((attachments) -> {
messageComposerViewModel.addSelectedAttachments(attachments);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAttachmentRemovalListener((attachment) -> {
messageComposerViewModel.removeSelectedAttachment(attachment);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setMentionSelectionListener((user) -> {
messageComposerViewModel.selectMention(user);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setCommandSelectionListener((command) -> {
messageComposerViewModel.selectCommand(command);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAlsoSendToChannelSelectionListener((checked) -> {
messageComposerViewModel.setAlsoSendToChannel(checked);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setDismissActionClickListener(() -> {
messageComposerViewModel.dismissMessageActions();
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setCommandsButtonClickListener(() -> {
messageComposerViewModel.toggleCommandsVisibility();
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setDismissSuggestionsListener(() -> {
messageComposerViewModel.dismissSuggestionsPopup();
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});
messageComposerView.setAttachmentsButtonClickListener(() -> {
// Handle attachments button click
return Unit.INSTANCE;
});Now let's see how to customize the view.
Customization
MessageComposerView can be customized:
- Using XML Attributes
- Using style Transformations
- By overriding content Views
Using XML Attributes
Many attributes of this View can be configured, like changing its color, the border and the color of the message input, fonts, components visibility, and so on. The full list of available attributes can be found here.
Here's an example of setting a custom attribute:
<io.getstream.chat.android.ui.message.composer.MessageComposerView
android:id="@+id/messageComposerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:streamUiMessageComposerMessageInputTextColor="#005AFF"
/>This produces the following styling:
Different configurations can be used to achieve the desired appearance of MessageComposerView. If you don't need to change this View appearance at runtime, XML should be enough. But if you need to able to customize it at runtime, then you can use MessageComposerViewStyle as described in the next section.
Using Style Transformations
You can use TransformStyle to apply global style transformations to all MessageComposerView instances. For example, you can create a messageComposerStyleTransformer like this one to change the input text color:
TransformStyle.messageComposerStyleTransformer = StyleTransformer { viewStyle ->
viewStyle.copy(
messageInputTextStyle = viewStyle.messageInputTextStyle.copy(
color = ContextCompat.getColor(context, R.color.stream_ui_accent_red)
)
)
}TransformStyle.setMessageComposerStyleTransformer(source -> {
// Customize the style
return source;
});The transformer should be set before the View is rendered to make sure that the new style was applied.
Overriding Content Views
With the new MessageComposerView you can replace certain parts of the layout with custom content views. There are several parts available for customization.
- Leading content: Represents the left part with integration buttons.
- Center content: Represents the center part with the text input.
- Trailing content: Represents the right part with the send button.
- Header content: Represents the top part with the action mode title.
- Footer content: Represents the bottom part with the "also send to channel" checkbox.
- Command suggestions content: Represents the content inside the command suggestions popup.
- Mention suggestions content: Represents the content inside the mention suggestions popup.
The available methods with the default content view implementations are listed below:
messageComposerView.setLeadingContent(
DefaultMessageComposerLeadingContent(context).also {
it.attachmentsButtonClickListener = { messageComposerView.attachmentsButtonClickListener() }
it.commandsButtonClickListener = { messageComposerView.commandsButtonClickListener() }
}
)
messageComposerView.setCenterContent(
DefaultMessageComposerCenterContent(context).also {
it.textInputChangeListener = { text -> messageComposerView.textInputChangeListener(text) }
it.attachmentRemovalListener = { attachment -> messageComposerView.attachmentRemovalListener(attachment) }
}
)
messageComposerView.setTrailingContent(
DefaultMessageComposerTrailingContent(context).also {
it.sendMessageButtonClickListener = { messageComposerView.sendMessageButtonClickListener() }
}
)
messageComposerView.setHeaderContent(
DefaultMessageComposerHeaderContent(context).also {
it.dismissActionClickListener = { messageComposerView.dismissActionClickListener() }
}
)
messageComposerView.setFooterContent(
DefaultMessageComposerFooterContent(context).also {
it.alsoSendToChannelSelectionListener =
{ checked -> messageComposerView.alsoSendToChannelSelectionListener(checked) }
}
)
messageComposerView.setCommandSuggestionsContent(
DefaultMessageComposerCommandSuggestionsContent(context).also {
it.commandSelectionListener =
{ command -> messageComposerView.commandSelectionListener(command) }
}
)
messageComposerView.setMentionSuggestionsContent(
DefaultMessageComposerMentionSuggestionsContent(context).also {
it.mentionSelectionListener = { user -> messageComposerView.mentionSelectionListener(user) }
}
)DefaultMessageComposerLeadingContent leadingContent = new DefaultMessageComposerLeadingContent(context);
leadingContent.setAttachmentsButtonClickListener(() -> messageComposerView.getAttachmentsButtonClickListener().invoke());
leadingContent.setCommandsButtonClickListener(() -> messageComposerView.getCommandsButtonClickListener().invoke());
messageComposerView.setLeadingContent(leadingContent);
DefaultMessageComposerCenterContent centerContent = new DefaultMessageComposerCenterContent(context);
centerContent.setTextInputChangeListener((text) -> messageComposerView.getTextInputChangeListener().invoke(text));
centerContent.setAttachmentRemovalListener((attachment -> messageComposerView.getAttachmentRemovalListener().invoke(attachment)));
messageComposerView.setCenterContent(centerContent);
DefaultMessageComposerTrailingContent trailingContent = new DefaultMessageComposerTrailingContent(context);
trailingContent.setSendMessageButtonClickListener(() -> messageComposerView.getSendMessageButtonClickListener().invoke());
messageComposerView.setTrailingContent(trailingContent);
DefaultMessageComposerHeaderContent headerContent = new DefaultMessageComposerHeaderContent(context);
headerContent.setDismissActionClickListener(() -> messageComposerView.getDismissActionClickListener().invoke());
messageComposerView.setHeaderContent(headerContent);
DefaultMessageComposerFooterContent footerContent = new DefaultMessageComposerFooterContent(context);
footerContent.setAlsoSendToChannelSelectionListener((checked) -> messageComposerView.getAlsoSendToChannelSelectionListener().invoke(checked));
messageComposerView.setFooterContent(footerContent);
DefaultMessageComposerCommandSuggestionsContent commandSuggestionsContent = new DefaultMessageComposerCommandSuggestionsContent(context);
commandSuggestionsContent.setCommandSelectionListener((command) -> messageComposerView.getCommandSelectionListener().invoke(command));
messageComposerView.setCommandSuggestionsContent(commandSuggestionsContent);
DefaultMessageComposerMentionSuggestionsContent mentionSuggestionsContent = new DefaultMessageComposerMentionSuggestionsContent(context);
mentionSuggestionsContent.setMentionSelectionListener((user) -> messageComposerView.getMentionSelectionListener().invoke(user));
messageComposerView.setMentionSuggestionsContent(mentionSuggestionsContent);To create a custom content view you need to create an Android View that implements the MessageComposerContent interface:
class CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent : FrameLayout, MessageComposerContent {
constructor(context: Context) : this(context, null)
constructor(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attrs, 0)
constructor(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : super(
context,
attrs,
defStyleAttr
)
override fun attachContext(messageComposerContext: MessageComposerContext) {
// Access the style if necessary
val style = messageComposerContext.style
}
override fun renderState(state: MessageComposerState) {
// Render the state of the component
}
}public class CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent extends FrameLayout implements MessageComposerContent {
public CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(@NonNull Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public void attachContext(@NonNull MessageComposerContext messageComposerContext) {
// Access the style if necessary
MessageComposerViewStyle style = messageComposerContext.getStyle();
}
@Override
public void renderState(@NonNull MessageComposerState state) {
// Render the state of the component
}
}Notice that you need to implement 2 methods from the MessageComposerContent interface:
attachContext()Called only once when the View has been attached to the hierarchy.renderState()Invoked when the state has changed and the UI needs to be updated accordingly.
Finally, you need to pass the created content view to the MessageComposerView:
messageComposerView.setLeadingContent(CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(context))CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent leadingContent = new CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(context);
messageComposerView.setLeadingContent(leadingContent);Here is an example of how the leading content can be customized to show a date picker button:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ImageView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/datePickerButton"
android:layout_width="24dp"
android:layout_height="24dp"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="8dp"
android:layout_marginVertical="16dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_calendar" />class CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent : FrameLayout, MessageComposerContent {
private lateinit var binding: CustomMessageComposerLeadingContentBinding
var datePickerButtonClickListener: () -> Unit = {}
constructor(context: Context) : this(context, null)
constructor(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attrs, 0)
constructor(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : super(
context,
attrs,
defStyleAttr
) {
binding = CustomMessageComposerLeadingContentBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(context), this, true)
binding.datePickerButton.setOnClickListener { datePickerButtonClickListener() }
}
override fun attachContext(messageComposerContext: MessageComposerContext) {
// Access the style if necessary
val style = messageComposerContext.style
}
override fun renderState(state: MessageComposerState) {
// Render the state of the component
}
}public class CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent extends FrameLayout implements MessageComposerContent {
private MessageComposerLeadingContentBinding binding;
public Function0<Unit> datePickerButtonClickListener = () -> null;
public CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(@NonNull Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
binding = MessageComposerLeadingContentBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(context), this, true);
binding.datePickerButton.setOnClickListener((view) -> {
datePickerButtonClickListener.invoke();
});
}
@Override
public void attachContext(@NonNull MessageComposerContext messageComposerContext) {
// Access the style if necessary
MessageComposerViewStyle style = messageComposerContext.getStyle();
}
@Override
public void renderState(@NonNull MessageComposerState state) {
// Render the state of the component
}
}messageComposerView.setLeadingContent(
CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(context).also {
it.datePickerButtonClickListener = {
val datePickerDialog = MaterialDatePicker.Builder
.datePicker()
.build()
datePickerDialog.addOnPositiveButtonClickListener {
// Handle date selection
}
datePickerDialog.show(fragmentManager, null)
}
}
)MaterialDatePicker<Long> datePickerDialog = MaterialDatePicker.Builder.datePicker().build();
datePickerDialog.addOnPositiveButtonClickListener(selection -> {
// Handle date selection
});
CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent leadingContent = new CustomMessageComposerLeadingContent(context);
leadingContent.datePickerButtonClickListener = () -> {
datePickerDialog.show(fragmentManager, null);
return Unit.INSTANCE;
};
messageComposerView.setLeadingContent(leadingContent);In the example above, we inflated a simple layout with just one date picker button and defined a listener to handle clicks on the button. A dialog is shown when the button is clicked.
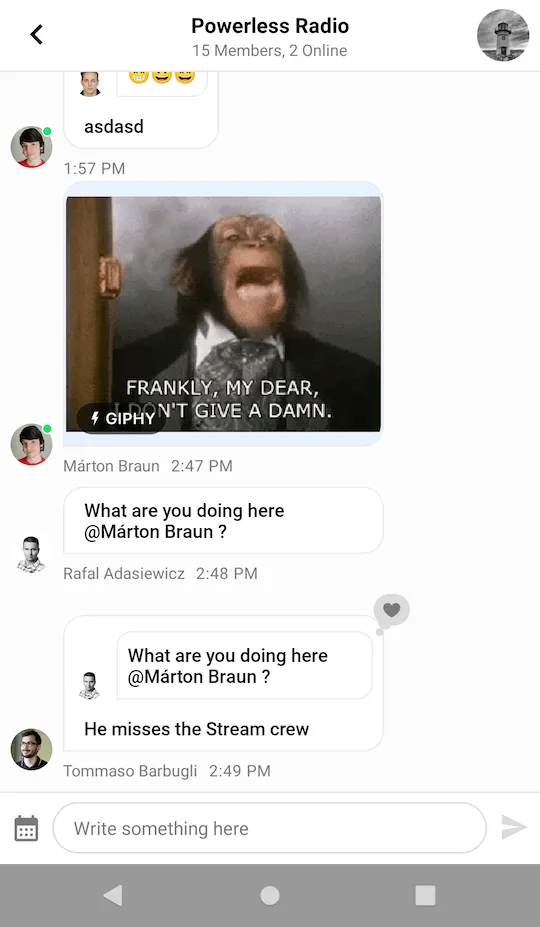 | 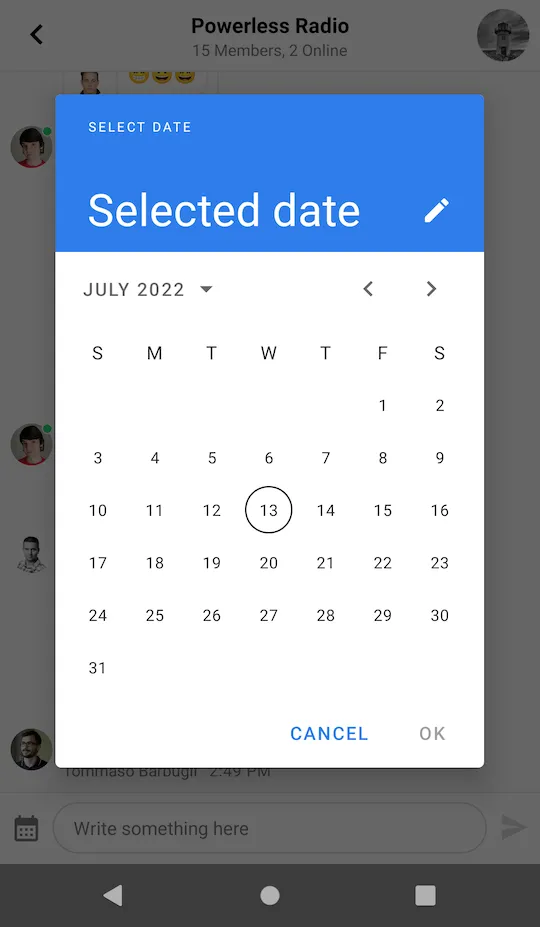 |