import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import { SafeAreaView, StyleSheet, Text } from "react-native";
import {
Call,
StreamCall,
CallContent,
CallingState,
StreamVideoClient,
StreamVideo,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
const apiKey = "REPLACE_WITH_API_KEY";
const token = "REPLACE_WITH_TOKEN";
const userId = "REPLACE_WITH_USER_ID";
const callId = "REPLACE_WITH_CALL_ID";
const user = {
id: userId,
name: "John Malkovich",
image: "https://robohash.org/John",
};
const client = new StreamVideoClient({ apiKey, user, token });
const RootContainer = (props: React.PropsWithChildren<{}>) => {
return <SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>{props.children}</SafeAreaView>;
};
export const App = () => {
const [call, setCall] = React.useState<Call>();
useEffect(() => {
const _call = client.call("default", callId);
_call.join({ create: true }).then(() => setCall(_call));
return () => {
_call.leave().catch(() => console.error("Failed to leave the call"));
setCall(undefined);
};
}, []);
if (!call) {
return (
<RootContainer>
<Text style={styles.text}>Joining call...</Text>
</RootContainer>
);
}
return (
<StreamVideo client={client}>
<StreamCall call={call}>
<RootContainer>
<CallContent />
</RootContainer>
</StreamCall>
</StreamVideo>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: "center",
backgroundColor: "white",
},
text: {
color: "black",
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: "bold",
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: "center",
},
});
export default App;Manual Video Quality Selection
The SDK automatically selects incoming video quality based on display size, avoiding bandwidth waste (e.g., receiving Full HD for a 320x240 display).
Override this behavior to manually request higher resolution for quality, lower resolution for bandwidth savings, or disable video for audio-only experience.
Best Practices
- Default to auto - Let the SDK optimize quality unless users need control
- Save preferences - Remember user's quality selection across sessions
- Show current setting - Display the active quality level clearly
- Explain tradeoffs - Help users understand bandwidth vs quality implications
Actual quality depends on source video quality and network conditions. Manual selection specifies preference; actual resolution is selected from available options to match as closely as possible.
This guide covers building a UI control for manual video quality selection.
Prerequisites
For a video calling application starting point, see the Video Calling Tutorial.
Basic application setup:
Getting and Setting Incoming Video Settings
Use the useIncomingVideoQualitySettings hook to get current settings:
- enabled - Boolean indicating whether incoming video is enabled
- preferredResolution - Object
{ width: number; height: number }containing preferred resolution (when video is enabled)
Modify settings using Call object methods:
- setIncomingVideoEnabled - Enable/disable incoming video, clearing preferred resolution
- setPreferredIncomingVideoResolution - Set preferred resolution, enabling video if previously disabled
Combine settings into a single control with mapping:
import type { Call } from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
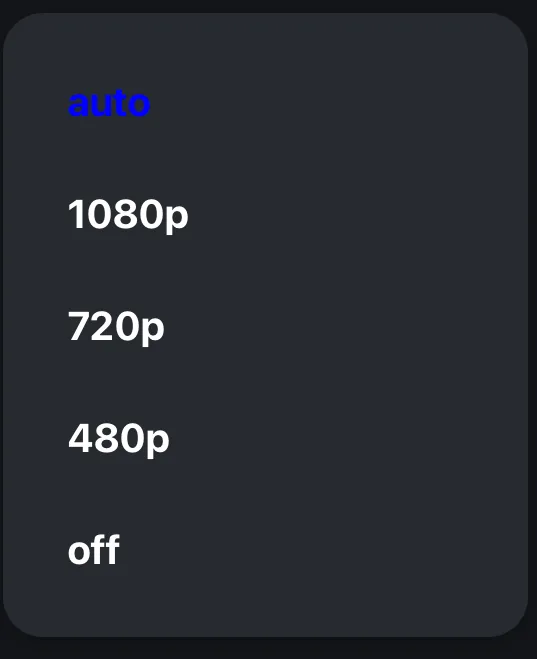
const incomingVideoSettings = ["auto", "1080p", "720p", "480p", "off"] as const;
type IncomingVideoSetting = (typeof incomingVideoSettings)[number];
type VideoDimension = { width: number; height: number };
const applyIncomingVideoSetting = (
call: Call,
setting: IncomingVideoSetting,
) => {
if (setting === "auto") {
call.setIncomingVideoEnabled(true);
} else if (setting === "off") {
call.setIncomingVideoEnabled(false);
} else {
call.setPreferredIncomingVideoResolution(
incomingVideoSettingToResolution(setting),
);
}
};
const incomingVideoSettingToResolution = (
setting: Exclude<IncomingVideoSetting, "auto" | "off">,
): VideoDimension => {
switch (setting) {
case "1080p":
return { width: 1920, height: 1080 };
case "720p":
return { width: 1280, height: 720 };
case "480p":
return { width: 640, height: 480 };
}
};
const incomingVideoResolutionToSetting = (
resolution: VideoDimension,
): IncomingVideoSetting => {
switch (true) {
case resolution.height >= 1080:
return "1080p";
case resolution.height >= 720:
return "720p";
case resolution.height >= 480:
return "480p";
default:
return "auto";
}
};Set preferred resolution per participant using the optional second parameter of setPreferredIncomingVideoResolution with an array of session IDs:
import { useCallStateHooks } from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
const { useParticipants } = useCallStateHooks();
const participants = useParticipants();
const [dominantParticipant] = participants;
call.setPreferredIncomingVideoResolution(
incomingVideoSettingToResolution("1080p"),
[dominantParticipant.sessionId],
);This guide applies preferred resolution to all call participants.
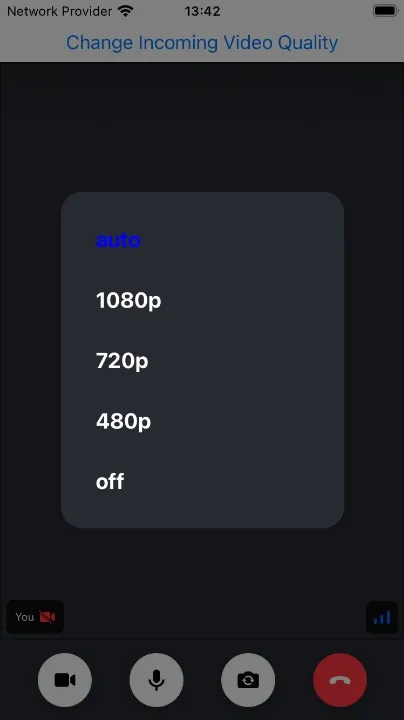
Building Incoming Video Quality Selector Button
Build a UI control using React Native's Modal component:
import {
useCall,
useCallStateHooks,
type Call,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { Button, Modal, Pressable, StyleSheet, Text, View } from "react-native";
/* This is the individual item inside the model */
const SettingSelectionItem = ({
value,
setValue,
selectedValue,
closeModal,
}: {
value: IncomingVideoSetting;
setValue: (setting: IncomingVideoSetting) => void;
selectedValue: IncomingVideoSetting;
closeModal: () => void;
}) => {
return (
<Pressable
onPress={() => {
setValue(value);
closeModal();
}}
style={styles.modalButton}
>
<Text
style={[
styles.modalText,
selectedValue === value ? styles.selectedModalText : null,
]}
>
{value}
</Text>
</Pressable>
);
};
/* This button that opens the modal along with the modal component */
export const IncomingVideoQualitySelectorButton = () => {
const [modalVisible, setModalVisible] = useState(false);
const closeModal = () => setModalVisible(false);
const call = useCall();
const { useIncomingVideoSettings } = useCallStateHooks();
const { enabled, preferredResolution } = useIncomingVideoSettings();
let currentSetting: IncomingVideoSetting;
if (!preferredResolution) {
currentSetting = enabled ? "auto" : "off";
} else {
currentSetting = incomingVideoResolutionToSetting(preferredResolution);
}
const handleChange = (setting: IncomingVideoSetting) => {
if (call) {
applyIncomingVideoSetting(call, setting);
}
};
return (
<>
<Modal
animationType="fade"
transparent
visible={modalVisible}
onRequestClose={closeModal}
>
<Pressable
style={styles.centeredView}
onPress={() => setModalVisible(false)}
>
<View style={styles.modalView} onStartShouldSetResponder={() => true}>
{incomingVideoSettings.map((setting) => (
<SettingSelectionItem
key={setting}
value={setting}
selectedValue={currentSetting}
setValue={handleChange}
closeModal={closeModal}
/>
))}
</View>
</Pressable>
</Modal>
{/* This is the button to open/close the modal */}
<Button
title="Change Incoming Video Quality"
onPress={() => setModalVisible(true)}
/>
</>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
centeredView: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)",
},
modalView: {
backgroundColor: "#272A30",
borderRadius: 20,
padding: 16,
alignItems: "flex-start",
shadowColor: "#000",
shadowOffset: {
width: 0,
height: 2,
},
shadowOpacity: 0.25,
shadowRadius: 4,
elevation: 5,
minWidth: "70%",
},
modalButton: {
padding: 16,
},
modalText: {
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: "bold",
color: "white",
},
selectedModalText: {
color: "blue",
},
});
Add the component inside StreamCall for a video quality selector button:
<StreamVideo client={client}>
<StreamCall call={call}>
<IncomingVideoQualitySelectorButton />
<SpeakerLayout />
</StreamCall>
</StreamVideo>