yarn add @react-native-firebase/app \
@react-native-firebase/messaging \
@notifee/react-native \
react-native-voip-push-notification \
react-native-callkeep
npx pod-installReact Native
If you are on version 1.2 or below, you would need to upgrade to 1.3 or above to follow the setup. As 1.3 release had breaking changes with respect to setting up of push notifications. We recommend to update to the current latest version.
This guide discusses how to add push notifications for ringing calls to your project. It will discuss both Android and iOS and go through all the necessary steps.
The normal user experience in a ringing app, when a user receives a call, is to show a push notification. The user can then interact with the notification to accept or reject the call. In this guide, you will learn how to set up your React Native app to get push notifications from Stream for the incoming calls that your user will receive.
| Android preview | iOS preview |
|---|---|
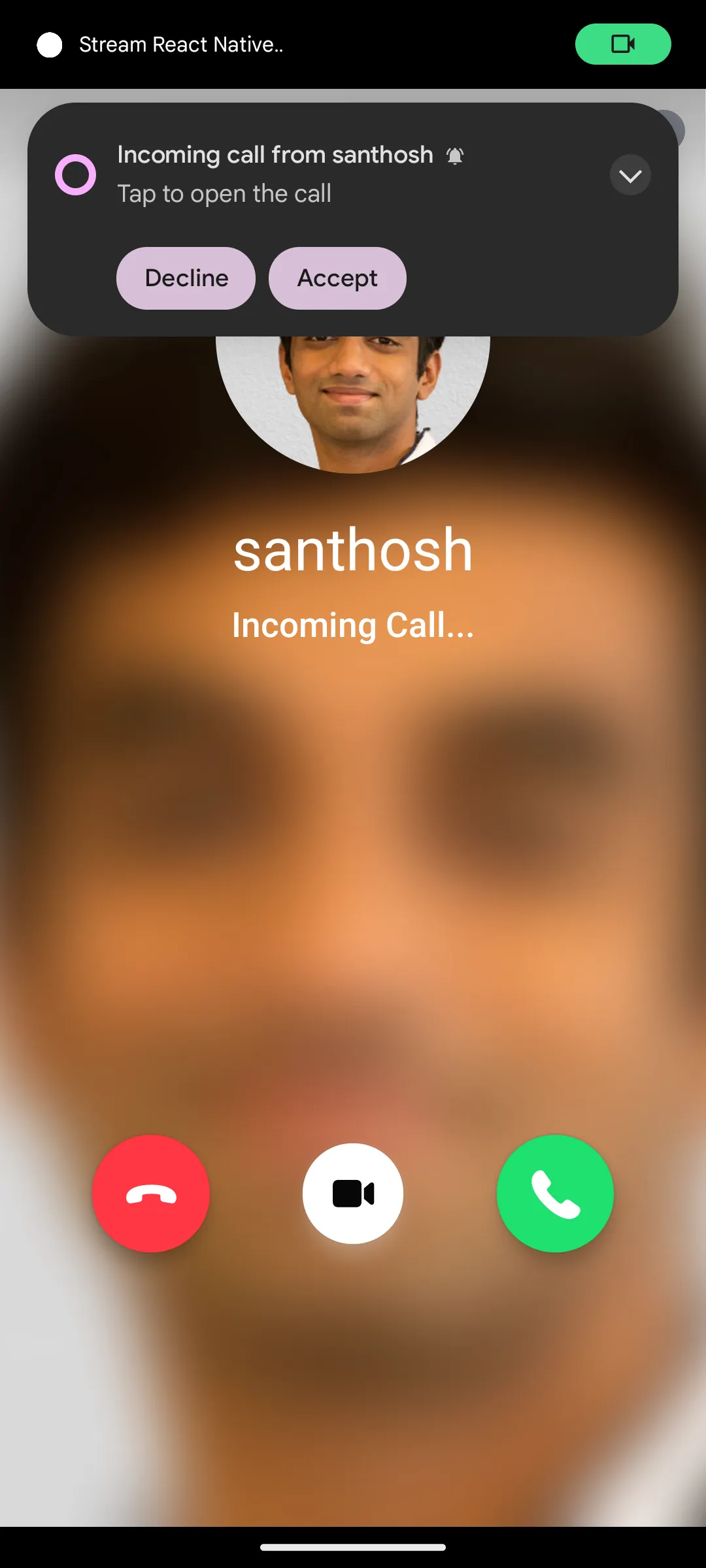 | 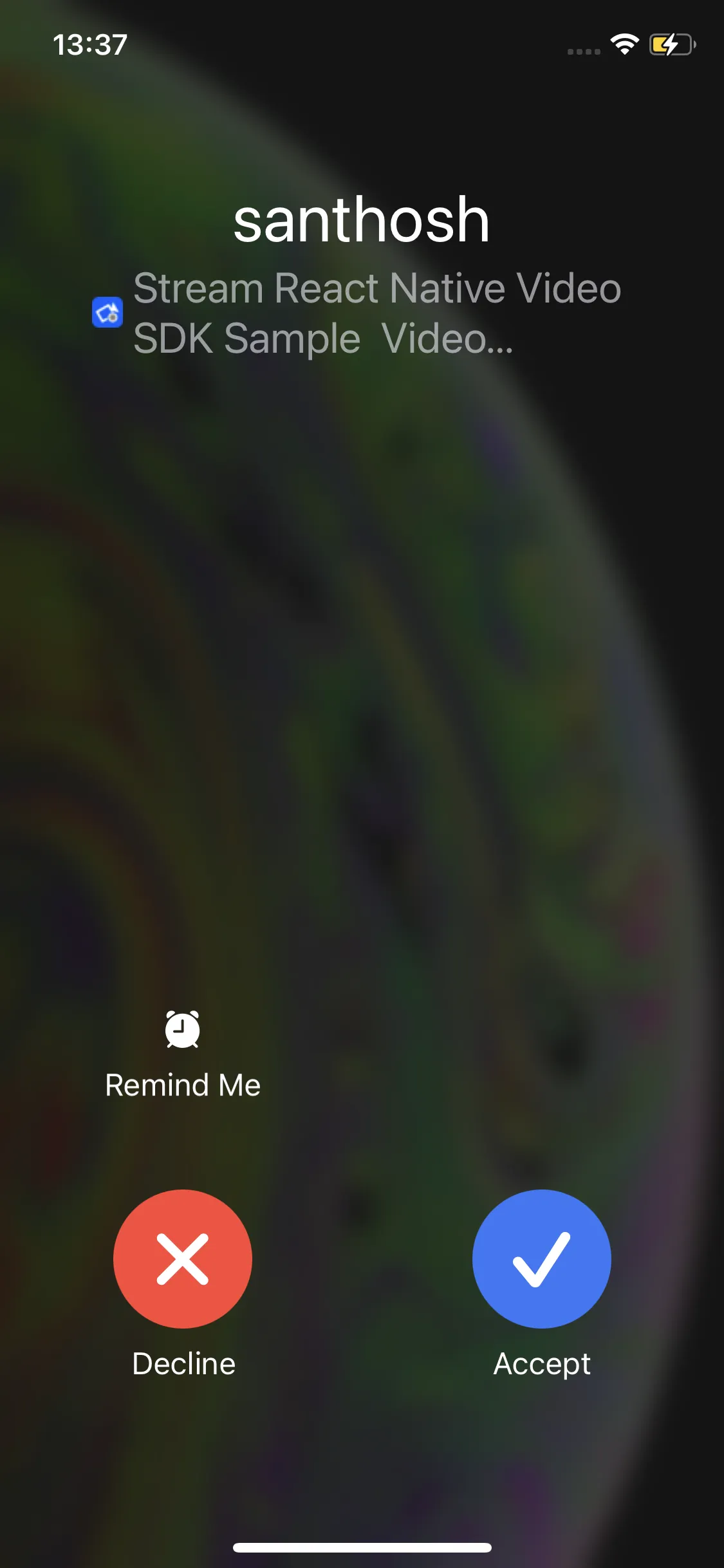 |
Full-screen notifications are displayed when the phone screen is locked or the app is active (foreground state). However, when the app is terminated or in the background and the screen is awake, notifications may appear as heads-up notifications instead of a full-screen alerts.
Add push provider credentials to Stream
Please follow the below guides for adding appropriate push providers to Stream:
- Android - Firebase Cloud Messaging
- iOS - Apple Push Notification Service (APNs)
Install Dependencies
So what did we install precisely?
@react-native-firebase/appand@react-native-firebase/messagingfor handling incoming Firebase Cloud Messaging notifications on Android.@notifee/react-native- is used to customize and display push notifications.react-native-voip-push-notificationfor handling incoming PushKit notifications on iOS.react-native-callkeepfor reporting incoming calls to iOS CallKit.
iOS-specific setup
Disable Firebase integration
We don’t use Firebase cloud messaging for iOS in the SDK. Unless Firebase is used for other purposes in your app,
you can safely remove it from being installed by iOS and avoid the auto-linking.
To do that create a file named react-native.config.js in the root of your project and add the following contents:
module.exports = {
dependencies: {
"@react-native-firebase/app": {
platforms: {
ios: null,
},
},
"@react-native-firebase/messaging": {
platforms: {
ios: null,
},
},
},
};Once this is done, run pod install again.
npx pod-installAdd background modes
In Xcode: Open Info.plist file and add the following in UIBackgroundModes. By editing this file with the text editor, you should see:
<key>BGTaskSchedulerPermittedIdentifiers</key>
<array>
<string>$(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)</string>
</array>
<key>UIBackgroundModes</key>
<array>
<string>audio</string>
<string>processing</string>
<string>remote-notification</string>
<string>voip</string>
</array>Enable push notifications
To receive push notifications, enable the Push Notifications capability in the Xcode Project > Signing & Capabilities pane.
Update AppDelegate
Update AppDelegate.m or AppDelegate.mm or AppDelegate.swift in Xcode with the following parts for iOS support.
Add headers
At the top of the file, add the following headers to import and invoke the methods for the required libraries.
#import <WebRTC/RTCAudioSession.h>
#import "RNCallKeep.h"
#import <PushKit/PushKit.h>
#import "RNVoipPushNotificationManager.h"
#import "StreamVideoReactNative.h"import RNCallKeep
import PushKit
import WebRTC
import RNVoipPushNotificationAdditionally, to import an Objective-C method you need to add the following import to your bridging header file:
#import "StreamVideoReactNative.h"If you dont have a bridging header file, you need to create one, see Apple’s documentation on Objective-C and Swift interoperability on how to create one through xcode.
Initialize on app launch
We need to set up the callkeep library and register VoIP at the app launch. To do this, add the following methods to your existing didFinishLaunchingWithOptions method,
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
NSString *localizedAppName = [[[NSBundle mainBundle] localizedInfoDictionary] objectForKey:@"CFBundleDisplayName"];
NSString *appName = [[[NSBundle mainBundle] infoDictionary]objectForKey :@"CFBundleDisplayName"];
[RNCallKeep setup:@{
@"appName": localizedAppName != nil ? localizedAppName : appName,
@"supportsVideo": @YES,
// pass @YES here if you want the call to be shown in calls history in the built-in dialer app
@"includesCallsInRecents": @NO,
}];
[RNVoipPushNotificationManager voipRegistration];
// the rest
}override func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey : Any]? = nil) -> Bool {
let localizedAppName = Bundle.main.localizedInfoDictionary?["CFBundleDisplayName"] as? String
let appName = Bundle.main.infoDictionary?["CFBundleDisplayName"] as! String
RNCallKeep.setup([
"appName": localizedAppName ?? appName,
"supportsVideo": true,
// pass true here if you want the call to be shown in calls history in the built-in dialer app
"includesCallsInRecents": false,
])
RNVoipPushNotificationManager.voipRegistration()
// the rest
}Add Audio Session methods
Add the following methods to call through the webrtc audioSessionDidActivate/Deactivate from CXProvider delegate accordingly:
- (void) provider:(CXProvider *) provider didActivateAudioSession:(AVAudioSession *) audioSession {
[[RTCAudioSession sharedInstance] audioSessionDidActivate:[AVAudioSession sharedInstance]];
}
- (void) provider:(CXProvider *) provider didDeactivateAudioSession:(AVAudioSession *) audioSession {
[[RTCAudioSession sharedInstance] audioSessionDidDeactivate:[AVAudioSession sharedInstance]];
}func provider(_ provider: CXProvider, didActivate audioSession: AVAudioSession) {
RTCAudioSession.sharedInstance().audioSessionDidActivate(AVAudioSession.sharedInstance())
}
func provider(_ provider: CXProvider, didDeactivate audioSession: AVAudioSession) {
RTCAudioSession.sharedInstance().audioSessionDidDeactivate(AVAudioSession.sharedInstance())
}Add PushKit methods
Add the following method to process the VoIP token from iOS and send it to the react-native-voip-push-notification library.
// handle updated push credentials
- (void)pushRegistry:(PKPushRegistry *)registry didUpdatePushCredentials:(PKPushCredentials *)credentials forType:(PKPushType)type {
[RNVoipPushNotificationManager didUpdatePushCredentials:credentials forType:(NSString *)type];
}// handle updated push credentials
func pushRegistry(
_ registry: PKPushRegistry,
didUpdate credentials: PKPushCredentials,
for type: PKPushType
) {
RNVoipPushNotificationManager.didUpdate(credentials, forType: type.rawValue)
}The final method to add is the one that gets invoked when there is a VoIP push notification from Stream.
When there is a push notification and the app is in the background, we want to display an incoming call notification. To achieve this, add the following method:
// handle incoming pushes
- (void)pushRegistry:(PKPushRegistry *)registry didReceiveIncomingPushWithPayload:(PKPushPayload *)payload forType:(PKPushType)type withCompletionHandler:(void (^)(void))completion {
// process the payload and store it in the native module's cache
NSDictionary *stream = payload.dictionaryPayload[@"stream"];
NSString *uuid = [[NSUUID UUID] UUIDString];
NSString *createdCallerName = stream[@"created_by_display_name"];
NSString *cid = stream[@"call_cid"];
NSString *videoIncluded = stream[@"video"];
BOOL hasVideo = [videoIncluded isEqualToString:@"false"] ? NO : YES;
// store the call cid and uuid in the native module's cache
[StreamVideoReactNative registerIncomingCall:cid uuid:uuid];
// set the completion handler - this one is called by the JS SDK
[RNVoipPushNotificationManager addCompletionHandler:uuid completionHandler:completion];
// send event to JS - the JS SDK will handle the rest and call the 'completionHandler'
[RNVoipPushNotificationManager didReceiveIncomingPushWithPayload:payload forType:(NSString *)type];
// display the incoming call notification
[RNCallKeep reportNewIncomingCall: uuid
handle: createdCallerName
handleType: @"generic"
hasVideo: hasVideo
localizedCallerName: createdCallerName
supportsHolding: NO
supportsDTMF: NO
supportsGrouping: NO
supportsUngrouping: NO
fromPushKit: YES
payload: stream
withCompletionHandler: nil];
}// handle incoming pushes
func pushRegistry(
_ registry: PKPushRegistry,
didReceiveIncomingPushWith payload: PKPushPayload,
for type: PKPushType,
completion: @escaping () -> Void
) {
// process the payload
guard
let stream = payload.dictionaryPayload["stream"] as? [String: Any],
let createdCallerName = stream["created_by_display_name"] as? String,
let cid = stream["call_cid"] as? String
else {
completion()
return
}
let uuid = UUID().uuidString
let videoIncluded = stream["video"] as? String
let hasVideo = videoIncluded == "false" ? false : true
StreamVideoReactNative.registerIncomingCall(cid, uuid: uuid)
RNVoipPushNotificationManager.addCompletionHandler(uuid, completionHandler: completion)
RNVoipPushNotificationManager.didReceiveIncomingPush(
with: payload,
forType: type.rawValue
)
// display the incoming call notification
RNCallKeep.reportNewIncomingCall(
uuid,
handle: createdCallerName,
handleType: "generic",
hasVideo: hasVideo,
localizedCallerName: createdCallerName,
supportsHolding: false,
supportsDTMF: false,
supportsGrouping: false,
supportsUngrouping: false,
fromPushKit: true,
payload: stream,
withCompletionHandler: nil
)
}Android-specific setup
- To create a Firebase project, go to the Firebase console and click on Add project.
- In the console, click the setting icon next to Project overview and open Project settings. Then, under Your apps, click the Android icon to open Add Firebase to your Android app and follow the steps. Make sure that the Android package name you enter is the same as the value of
android.packagefrom your app.json. - After registering the app, download the google-services.json file and place it inside your project at the following location:
/android/app/google-services.json. - To allow Firebase on Android to use the credentials, the
google-servicesplugin must be enabled on the project. This requires modification to two files in the Android directory. Add the highlighted lines in the relevant files:
buildscript {
dependencies {
// ... other dependencies
classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.15'
}
}apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'The google-services.json file contains unique and non-secret identifiers of your Firebase project. For more information, see Understand Firebase Projects.
Update AndroidManifest.xml
Add the following in AndroidManifest.xml:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.POST_NOTIFICATIONS" />
<!-- We declare the permissions needed for using foreground service to keep call alive -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MICROPHONE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CONNECTED_DEVICE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_DATA_SYNC" />
<service
android:name="app.notifee.core.ForegroundService"
tools:replace="android:foregroundServiceType"
android:stopWithTask="true"
android:foregroundServiceType="shortService|dataSync|camera|microphone|connectedDevice"
/>The foreground service and its permissions are essential for displaying incoming call notifications when the app is running in the background, as well as for maintaining video and audio calls during background operation. When uploading the app to the Play Store, it is necessary to declare the foreground service permissions in the Play Console and provide an explanation of their usage. This includes adding a link to a video that demonstrates how the foreground service is utilized for video and audio calls. This procedure is required only once. For more details, refer to here.
The permissions to be explained are:
android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CAMERA- To access camera when app goes to backgroundandroid.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MICROPHONE- To access microphone when app goes to backgroundandroid.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CONNECTED_DEVICE- To access bluetooth headsets when app goes to backgroundandroid.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_DATA_SYNC- To keep video/audio calls alive when both camera and microphone access permissions were not granted
Request for notification permission
At an appropriate place in your app, request for notification permissions from the user.
Below is a an example of how to request permissions using the react-native-permissions library:
import { requestNotifications } from "react-native-permissions";
await requestNotifications(["alert", "sound"]);Add Firebase message handlers
To process the incoming push notifications, the SDK provides the utility functions that you must add to your existing or new Firebase notification listeners. Below is the snippet of how to add the firebase listeners:
import messaging from "@react-native-firebase/messaging";
import notifee from "@notifee/react-native";
import {
isFirebaseStreamVideoMessage,
firebaseDataHandler,
onAndroidNotifeeEvent,
isNotifeeStreamVideoEvent,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
export const setFirebaseListeners = () => {
// Set up the background message handler
messaging().setBackgroundMessageHandler(async (msg) => {
if (isFirebaseStreamVideoMessage(msg)) {
await firebaseDataHandler(msg.data);
} else {
// your other background notifications (if any)
}
});
// on press handlers of background notifications
notifee.onBackgroundEvent(async (event) => {
if (isNotifeeStreamVideoEvent(event)) {
await onAndroidNotifeeEvent({ event, isBackground: true });
} else {
// your other background notifications (if any)
}
});
// Optionally: set up the foreground message handler
messaging().onMessage((msg) => {
if (isFirebaseStreamVideoMessage(msg)) {
firebaseDataHandler(msg.data);
} else {
// your other foreground notifications (if any)
}
});
// Optionally: on press handlers of foreground notifications
notifee.onForegroundEvent((event) => {
if (isNotifeeStreamVideoEvent(event)) {
onAndroidNotifeeEvent({ event, isBackground: false });
} else {
// your other foreground notifications (if any)
}
});
};Firebase message handlers:
- The
onMessagehandler should not be added if you do not want notifications to show up when the app is in the foreground. When the app is in foreground, you would automatically see the incoming call screen. - The
isFirebaseStreamVideoMessagemethod is used to check if this push message is a video related message. And only this needs to be processed by the SDK. - The
firebaseDataHandlermethod is the callback to be invoked to process the message. This callback reads the message and uses the@notifee/react-nativelibrary to display push notifications.
Notifee event handlers:
- The
onForegroundEventhandler should not be added if you did not add foreground notifications above. - The
isNotifeeStreamVideoEventmethod is used to check if the event was a video related notifee event. And only this needs to be processed by the SDK. - The
onAndroidNotifeeEventmethod is the callback to be invoked to process the event. This callback reads the event and makes sure that the call is accepted or declined.
If you had disabled the installation of Firebase on iOS, add the above method only for Android using the Platform-specific extensions for React Native.
For example, say you add the following files in your project:
setFirebaseListeners.android.ts
setFirebaseListeners.tsThe method above must only be added to the file that .android extension. The other file must add the method but do nothing like below:
export const setFirebaseListeners = () => {
// do nothing
};This is to ensure that @react-native-firebase/messaging is only imported on the Android platform.
Setup the push notifications configuration for the SDK
The SDK automatically processes the incoming push notifications once the setup above is done if the push notifications configuration has been set using StreamVideoRN.setPushConfig.
Through this method, you can override the default notification texts and set the push provider name for both iOS and Android and provide your custom ringtone.
Below is an example of how this method can be called:
import {
StreamVideoClient,
StreamVideoRN,
User,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
import { AndroidImportance } from "@notifee/react-native";
import AsyncStorage from "@react-native-async-storage/async-storage";
import { STREAM_API_KEY } from "../../constants";
export function setPushConfig() {
StreamVideoRN.setPushConfig({
ios: {
// add your push_provider_name for iOS that you have setup in Stream dashboard
pushProviderName: __DEV__ ? "apn-video-staging" : "apn-video-production",
},
android: {
// the name of android notification icon (Optional, defaults to 'ic_launcher')
smallIcon: "ic_notification",
// add your push_provider_name for Android that you have setup in Stream dashboard
pushProviderName: __DEV__
? "firebase-video-staging"
: "firebase-video-production",
// configure the notification channel to be used for incoming calls for Android.
incomingCallChannel: {
id: "stream_incoming_call",
name: "Incoming call notifications",
// This is the advised importance of receiving incoming call notifications.
// This will ensure that the notification will appear on-top-of applications.
importance: AndroidImportance.HIGH,
// optional: if you dont pass a sound, default ringtone will be used
sound: "<url to the ringtone>",
},
// configure the functions to create the texts shown in the notification
// for incoming calls in Android.
incomingCallNotificationTextGetters: {
getTitle: (userName: string) => `Incoming call from ${userName}`,
getBody: (_userName: string) => "Tap to answer the call",
getAcceptButtonTitle: () => "Accept",
getDeclineButtonTitle: () => "Decline",
},
},
// add the async callback to create a video client
// for incoming calls in the background on a push notification
createStreamVideoClient: async () => {
const userId = await AsyncStorage.getItem("@userId");
const userName = await AsyncStorage.getItem("@userName");
if (!userId) return undefined;
// an example promise to fetch token from your server
const tokenProvider = async (): Promise<string> =>
yourServerAPI.getTokenForUser(userId).then((auth) => auth.token);
const user: User = { id: userId, name: userName };
return StreamVideoClient.getOrCreateInstance({
apiKey: STREAM_API_KEY, // pass your stream api key
user,
tokenProvider,
});
},
});
}It is essential that StreamVideoClient.getOrCreateInstance(..) is always used to get a existing StreamVideoClient instance in your app instead of always creating a new instance with new StreamVideoClient(..). Reusing the client instance makes sure that the accept/decline states of the call that are changed while app was in the background is preserved. The getOrCreateInstance method ensures that for the same user the instance is reused.
We highly recommend that android.smallIcon is set. To quickly and easily generate small icons with the correct settings, we recommend using the Android Asset Studio.
Initialize SDK push notification methods
Call the methods we have created outside your application cycle.
That is, alongside your AppRegistry.registerComponent() method call at the entry point of your application code.
We do this because the app can be opened from a dead state through a push notification, and in that case, we need to use the configuration and notification callbacks as soon as the JS bridge is initialized.
import { AppRegistry } from "react-native";
import { setPushConfig } from "src/utils/setPushConfig";
import { setFirebaseListeners } from "src/utils/setFirebaseListeners";
import App from "./App";
setPushConfig(); // Set push config
setFirebaseListeners(); // Set the firebase listeners
AppRegistry.registerComponent("app", () => App);Disabling push notifications
In some cases, you would want to disable the delivery of push notifications. One example is the user logs out of your app or, if you switch an user on the device.
import { StreamVideoRN } from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
await StreamVideoRN.onPushLogout();Optional: Android full-screen incoming call view on locked phone
To display a full-screen notification for the incoming call when the phone is locked, add the following code in onCreate to your main activity:
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ..the rest
super.onCreate()
// Add this
StreamVideoReactNative.setupCallActivity(this)
}@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// ..the rest
super.onCreate();
// Add this
StreamVideoReactNative.setupCallActivity(this);
}Also, in the AndroidManifest.xml add the following permission above the <application> section:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT" />For apps installed on phones running versions Android 13 or lower, the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT permission is enabled by default.
For all apps being installed on Android 14 and above, the Google Play Store revokes the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT for apps that do not have calling or alarm functionalities. Which means, while submitting your app to the play store, if you do declare that ‘Making and receiving calls’ is a ‘core’ functionality in your app, this permission is granted by default on Android 14 and above.
If the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT permission is not granted, the notification will show up as an expanded heads up notification on the lock screen.
Incoming and Outgoing call UI in foreground
The last part of the setup for ringing calls is to show the incoming and outgoing call UIs in the app whenever there is a ringing call. If this was not implemented before, please visit this page of our documentation to implement that.
Troubleshooting
Check our Troubleshooting guide for solutions to common mistakes.
- Add push provider credentials to Stream
- Install Dependencies
- iOS-specific setup
- Android-specific setup
- Setup the push notifications configuration for the SDK
- Initialize SDK push notification methods
- Disabling push notifications
- Optional: Android full-screen incoming call view on locked phone
- Incoming and Outgoing call UI in foreground
- Troubleshooting