dependencies:
stream_video_filters: ^latestVideo filters
A very common use case during a video call is to apply some effect on our backgrounds. Those backgrounds can vary but the most common ones are blurring and adding a static image. Our SDK offers background blurring and virtual backgrounds with static images out of the box and also has support for injecting your custom filter into the calling experience. In this guide, we will show you how to apply video filters to a video stream.
Using the background video filters provided by the SDK
Step 1 - Adding the dependency
Video filters are part of a separate stream_video_filters package so make sure you have it in your app's pubspec.yaml
The package adds the required native modules for processing the video stream and manipulating it with your desired video filter.
Step 2 - Use the StreamVideoEffectsManager to control the filters
Background filters are controlled using StreamVideoEffectsManager. It is responsible for making sure relevant processors are registered and for applying and disabling filters to the video track.
A basic usage looks like this:
import 'package:stream_video_filters/video_effects_manager.dart';
final videoEffectsManager = StreamVideoEffectsManager(call);
// Apply blur effect
videoEffectsManager.applyBackgroundBlurFilter(BlurIntensity.light);
videoEffectsManager.applyBackgroundBlurFilter(BlurIntensity.medium);
videoEffectsManager.applyBackgroundBlurFilter(BlurIntensity.heavy);
// Apply virtual background effect
videoEffectsManager.applyBackgroundImageFilter('assets/backgroundImage.jpg')
videoEffectsManager.applyBackgroundImageFilter('https://picsum.photos/id/192/2352/2352')
// Disable all applied filters
videoEffectsManager.disableAllFilters();In iOS, the background video filters are supported only on iOS 15 and above. However, the iOS platform's minimum level of support for the custom filters that you may add depends on what APIs you would use.
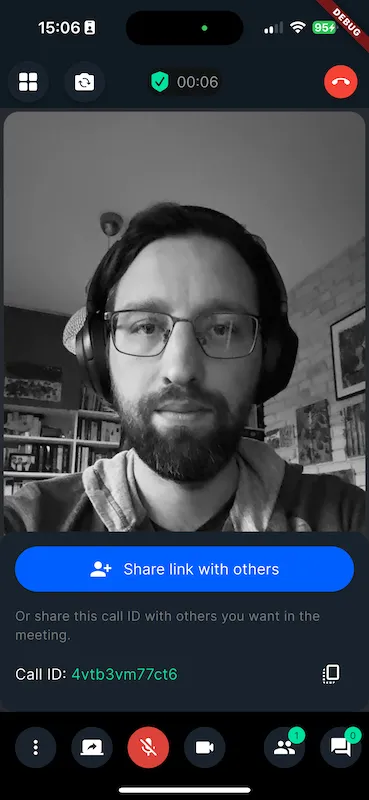
| Preview of background blur filter | Preview of background image replacement filter |
|---|---|
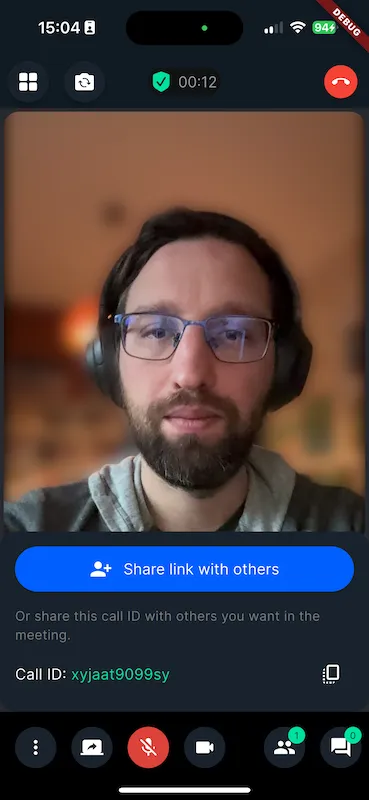 | 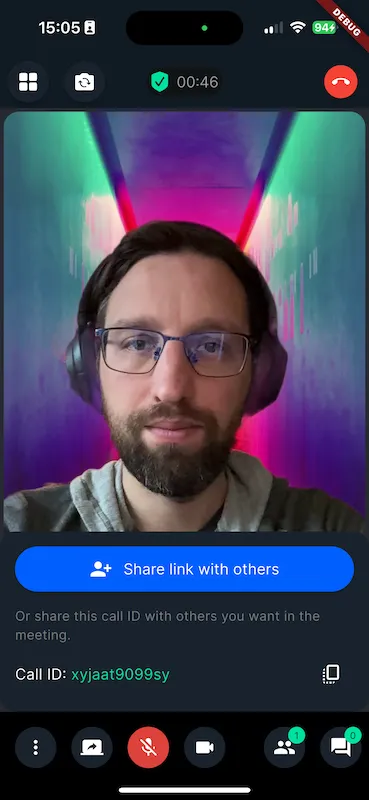 |
Advanced: adding custom video filters
Step 1 - Add your custom filter natively in Android and iOS
To create a new video filter, you need to implement the VideoFrameProcessorFactoryInterface from stream_webrtc_flutter package. A simple example that applies rotation to the video filter would be like the following:
import io.getstream.webrtc.flutter.videoEffects.VideoFrameProcessor
import io.getstream.webrtc.flutter.videoEffects.VideoFrameProcessorFactoryInterface
import org.webrtc.VideoFrame
class RotationFilterFactory : VideoFrameProcessorFactoryInterface {
override fun build(): VideoFrameProcessor {
return VideoFrameProcessor { frame, textureHelper ->
VideoFrame(
frame.buffer.toI420(),
180, // apply rotation to the video frame
frame.timestampNs
)
}
}
}To implement a video filter with Bitmap, create a class by extending a filter that extends from BitmapVideoFilter abstract class. This BitmapVideoFilter abstract class gives you a Bitmap for each video frame, which you can manipulate directly. By returning a new VideoFrameProcessorWithBitmapFilter instance with that filter we can implement a bitmap processing filter.
BitmapVideoFilter is less performant than a normal video filter that does not use bitmaps. It is due to the overhead of certain operations, like YUV <-> ARGB conversions.
Example: grayscale video filter
We can create and set a simple video filter that turns the video frame to grayscale by extending a filter that extends from BitmapVideoFilter abstract class like this:
import android.graphics.Bitmap
import android.graphics.Canvas
import android.graphics.ColorMatrix
import android.graphics.ColorMatrixColorFilter
import android.graphics.Paint
import io.getstream.webrtc.flutter.videoEffects.VideoFrameProcessor
import io.getstream.webrtc.flutter.videoEffects.VideoFrameProcessorFactoryInterface
import io.getstream.video.flutter.stream_video_filters.common.VideoFrameProcessorWithBitmapFilter
import io.getstream.video.flutter.stream_video_filters.common.BitmapVideoFilter
class GrayScaleVideoFilterFactory : VideoFrameProcessorFactoryInterface {
override fun build(): VideoFrameProcessor {
return VideoFrameProcessorWithBitmapFilter {
GrayScaleFilter()
}
}
}
private class GrayScaleFilter : BitmapVideoFilter() {
override fun applyFilter(videoFrameBitmap: Bitmap) {
val canvas = Canvas(videoFrameBitmap)
val paint = Paint().apply {
val colorMatrix = ColorMatrix().apply {
// map the saturation of the color to grayscale
setSaturation(0f)
}
colorFilter = ColorMatrixColorFilter(colorMatrix)
}
canvas.drawBitmap(videoFrameBitmap, 0f, 0f, paint)
}
}To add a new video filter, you need to specify an object that conforms to the VideoFrameProcessorDelegate protocol from the stream_webrtc_flutter library and inherits from the NSObject class.
You can implement the filter using the VideoFilter class. You will receive each frame of the user's local video as CIImage, allowing you to apply the filters. The VideoFilter class allows you to easily create your own filters. It contains the function that converts the original CIImage to an output CIImage. This way you have complete freedom over the processing pipeline. Instead, if you would need to access the raw video frame you can look into the implementation of VideoFilter class and adapt it to your own filter.
Example: grayscale video filter
We can create and set a simple video filter that turns the video frame to grayscale by extending a filter class that extends from VideoFilter class like this:
import Foundation
import stream_video_filters
final class GrayScaleVideoFrameProcessor: VideoFilter {
@available(*, unavailable)
override public init(
filter: @escaping (Input) -> CIImage
) { fatalError() }
init() {
super.init(
filter: { input in
let filter = CIFilter(name: "CIPhotoEffectMono")
filter?.setValue(input.originalImage, forKey: kCIInputImageKey)
let outputImage: CIImage = filter?.outputImage ?? input.originalImage
return outputImage
}
)
}
}Step 2 - Register this filter in your native module
Now you have to add a method in your app to register this video filter in the stream_webrtc_flutter library. The registration is done on the native side but it has to be accessed from your app's Dart code. To accomplish this we will use platform channel.
First, create a MethodChannel on the Dart side:
static const platform = MethodChannel('sample.app.channel');
Future<void> registerGreyscaleEffect() async {
await platform.invokeMethod('registerGreyscaleEffect');
}Then implement the corresponding methods on the native side. This code will register the previously created grayscale filter into ProcessorProvider and enable its usage later.
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.plugins.FlutterPlugin
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.plugins.activity.ActivityAware
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.plugins.activity.ActivityPluginBinding
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel
import io.flutter.plugin.common.PluginRegistry
import io.getstream.webrtc.flutter.videoEffects.ProcessorProvider
class MainActivity: FlutterActivity() {
private val CHANNEL = "sample.app.channel"
override fun configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine: FlutterEngine) {
super.configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine)
MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler { call, result ->
if (call.method == "registerGreyscaleEffect") {
ProcessorProvider.addProcessor("grayscale", GrayScaleVideoFilterFactory())
result.success(null)
} else {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
}
}@UIApplicationMain
@objc class AppDelegate: FlutterAppDelegate {
private let CHANNEL = "sample.app.channel"
override func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?
) -> Bool {
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.register(with: self)
let controller = window?.rootViewController as! FlutterViewController
let channel = FlutterMethodChannel(
name: CHANNEL, binaryMessenger: controller.binaryMessenger)
channel.setMethodCallHandler { [weak self] (call, result) in
self?.handleMethodCall(call: call, result: result)
}
return super.application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)
}
func handleMethodCall(call: FlutterMethodCall, result: @escaping FlutterResult) {
if call.method == "registerGreyscaleEffect" {
ProcessorProvider.addProcessor(GrayScaleVideoFrameProcessor(), forName: "grayscale")
result(nil)
} else {
result(FlutterMethodNotImplemented)
}
}
}It is important to use the @objc modifiers to ensure the class and functions are exported properly to the Objective-C runtime.
NOTE
While calling the addProcessor method. We need to provide a name to the filter that we are registering. In the above example, it is grayscale. This name will be later used when appling the filter.
Step 3 - Apply the video filter in Dart
To apply this video filter, simply call the applyCustomEffect() method on the StreamVideoEffectsManager instance, providing the name of the previously registered video processor (in this case, grayscale). Additionally, you need to pass the registerEffectProcessorCallback, which will be invoked to register the processor on the native side. We will use the previously created registerGreyscaleEffect() method that utilizes the method channel for this purpose.
final videoEffectsManager = StreamVideoEffectsManager(call);
// Apply custom video filter
videoEffectsManager.applyCustomEffect(
'grayscale',
registerEffectProcessorCallback: () async {
await registerGreyscaleEffect();
});
// Disable all applied filters
videoEffectsManager.disableAllFilters();Below is a preview of the above grayscale video filter: