import React from "react";
import { CallContent } from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
import { StyleSheet, View } from "react-native";
export const ActiveCall = () => {
// other code omitted for brevity
const { theme } = useTheme();
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<CallContent
onHangupCallHandler={onHangupCallHandler}
landscape={currentOrientation === "landscape"}
layout={selectedLayout}
/>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: { flex: 1 },
});Safe Area Insets
Introduction
Mobile applications must avoid overlapping UI elements with system components: status bars, notches, home indicators, and navigation bars.
Best Practices
- Always use safe area insets - Prevent content from being obscured by system UI
- Test on multiple devices - Different devices have varying safe area requirements
- Handle orientation changes - Safe areas differ between portrait and landscape
- Apply insets consistently - Use theme-level configuration for uniform spacing
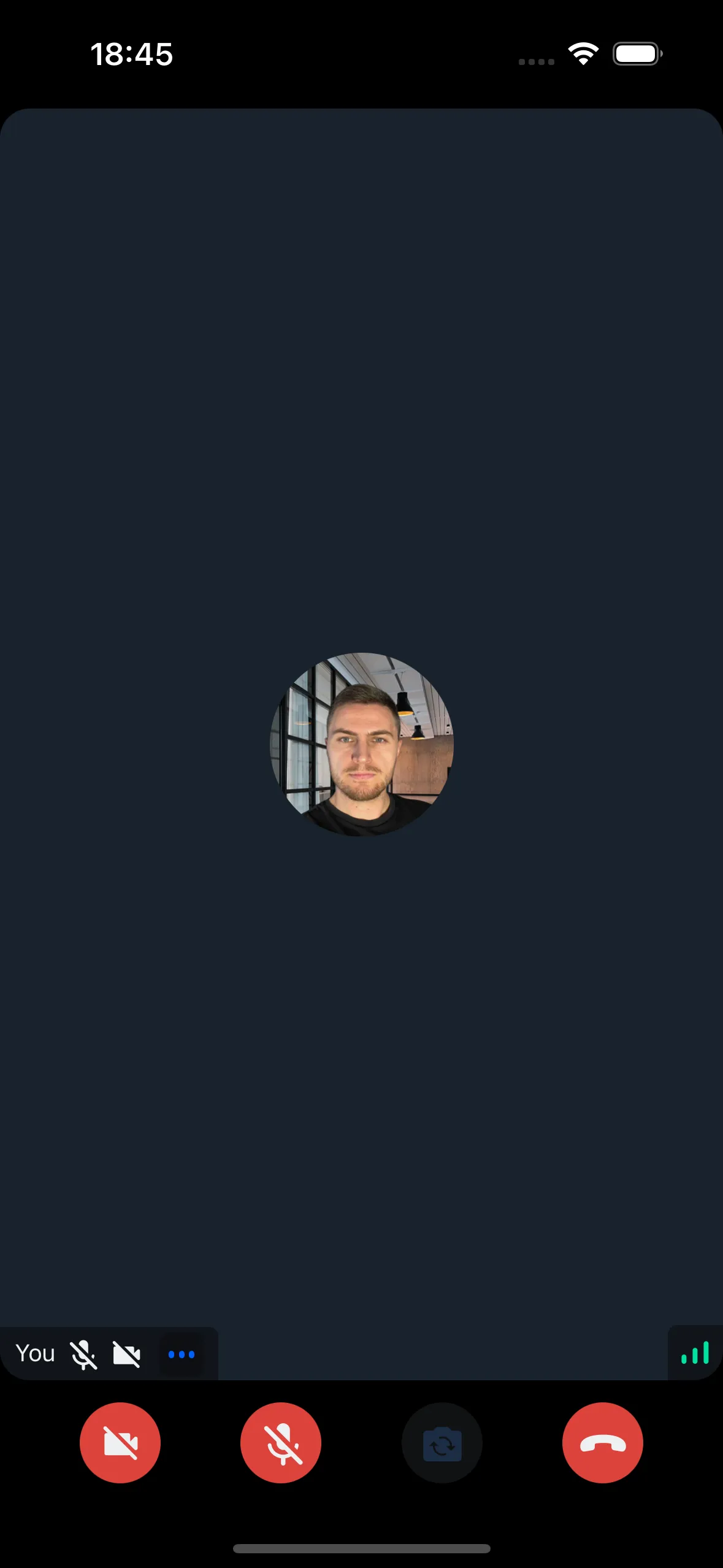
The Problem
A basic call content component without safe area handling:
Result: UI elements overlap with system areas:
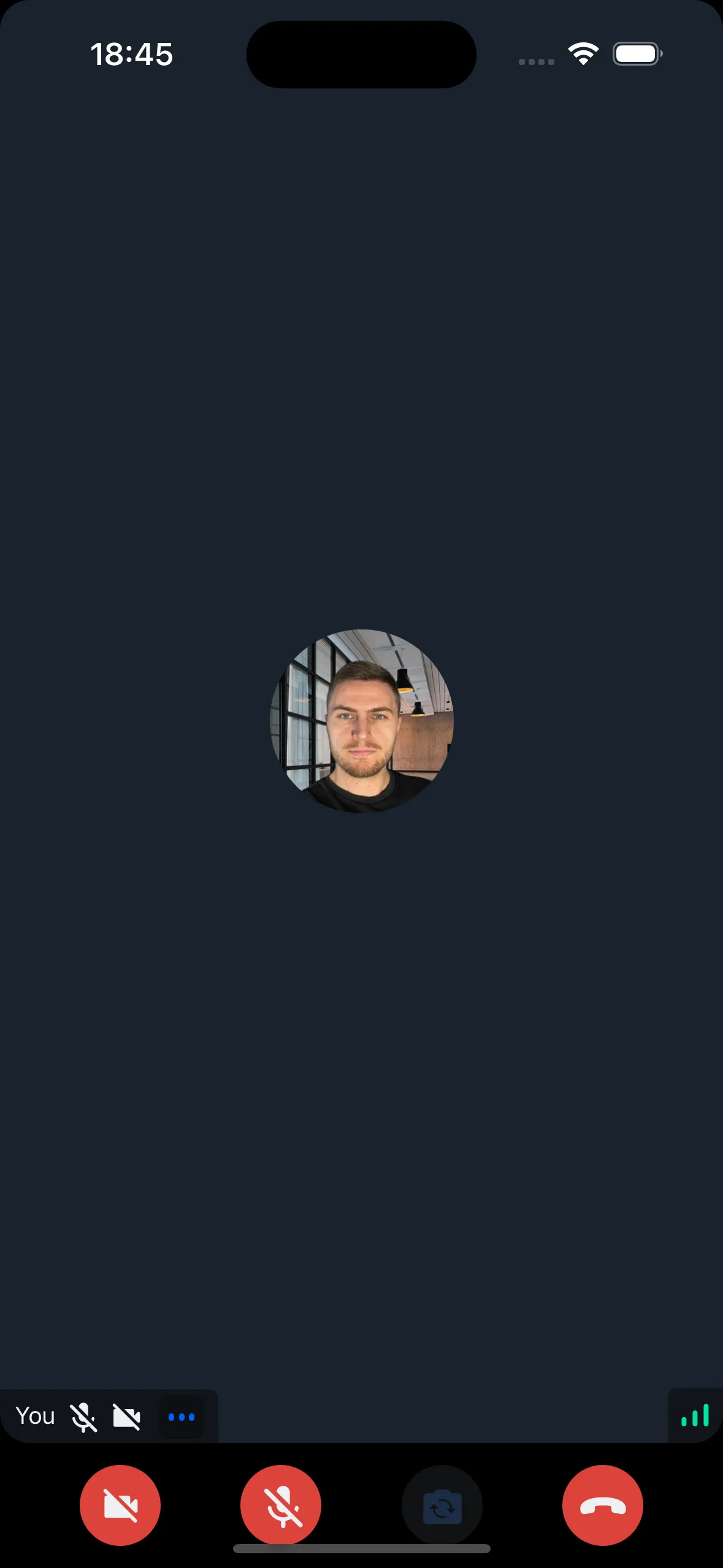
The Solution
Use insets from react-native-safe-area-context. This package automatically calculates padding values based on the device's notch, home indicator, and status bar.
react-native-safe-area-context is included by default in Expo. For non-Expo projects:
npm install react-native-safe-area-contextOverride the default insets in your theme:
import { DeepPartial, Theme } from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
import { useSafeAreaInsets } from "react-native-safe-area-context";
export const useCustomTheme = (): DeepPartial<Theme> => {
const { top, right, bottom, left } = useSafeAreaInsets();
const variants: DeepPartial<Theme["variants"]> = {
insets: {
top,
right,
bottom,
left,
},
};
const customTheme: DeepPartial<Theme> = {
variants,
};
return customTheme;
};Provide the custom theme to the style prop of StreamVideo:
import {
StreamVideo,
StreamVideoClient,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
import { useCustomTheme } from "../theme";
export const App = () => {
const client = new StreamVideoClient(/* ... */);
const customTheme = useCustomTheme();
return (
<StreamVideo client={client} style={customTheme}>
<MyUI />
</StreamVideo>
);
};Alternatively, pass the prop to StreamTheme to wrap specific components:
// ... same code
return (
<StreamVideo client={client}>
<StreamTheme style={customTheme}>
<MyUI />
</StreamTheme>
</StreamVideo>
);Without additional code changes, the insets are properly applied: