npx expo install @react-native-firebase/app
npx expo install @react-native-firebase/messaging
npx expo install @notifee/react-native
npx expo install react-native-voip-push-notification
npx expo install react-native-callkeep @config-plugins/react-native-callkeepExpo
If you are on version 1.2 or below, you would need to upgrade to 1.3 or above to follow the setup. As 1.3 release had breaking changes with respect to setting up of push notifications. We recommend to update to the current latest version.
This guide discusses how to add push notifications for ringing calls to your project. It will discuss both Android and iOS and go through all the necessary steps.
The normal user experience in a ringing app, when a user receives a call, is to show a push notification. The user can then interact with the notification to accept or reject the call. In this guide, you will learn how to set up your Expo app to get push notifications from Stream for the incoming calls that your user will receive.
| Android preview | iOS preview |
|---|---|
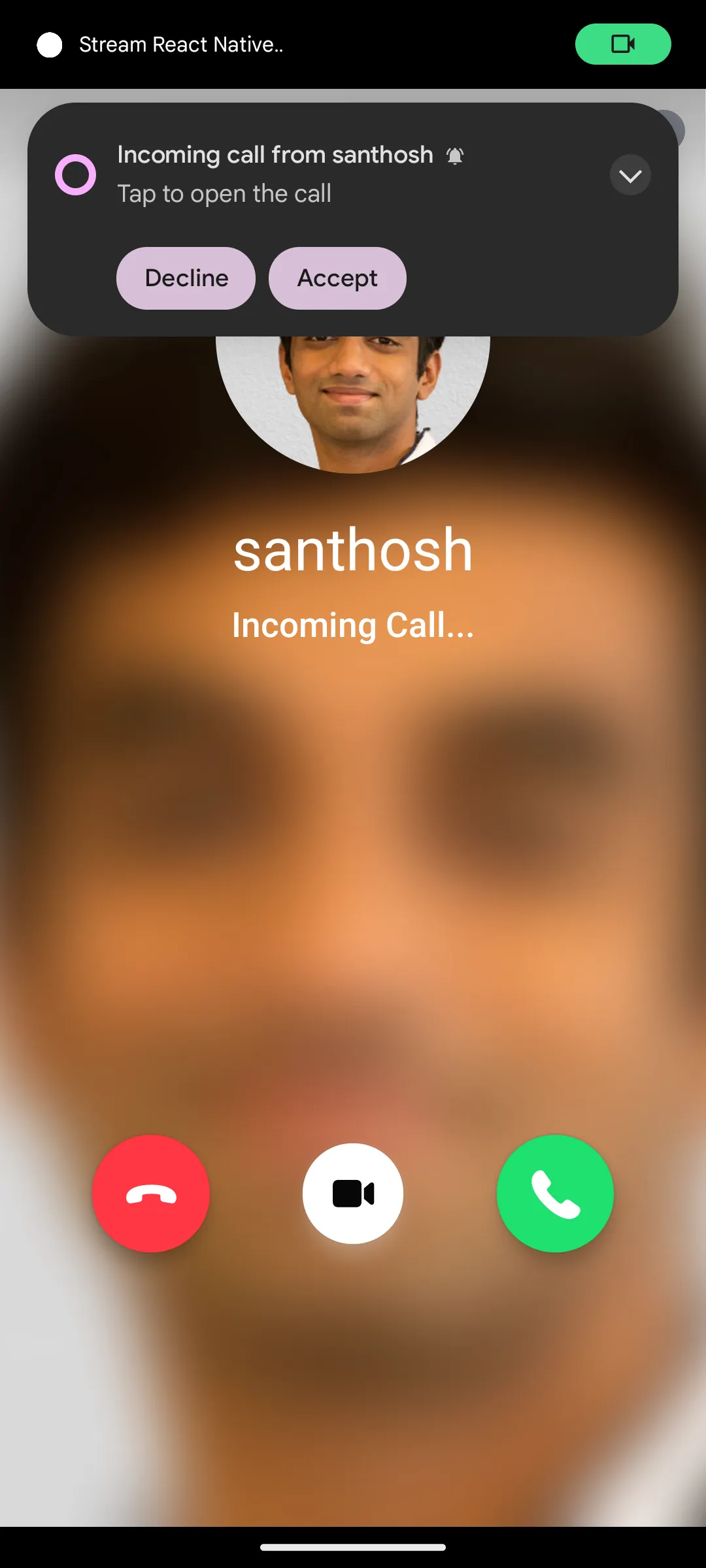 | 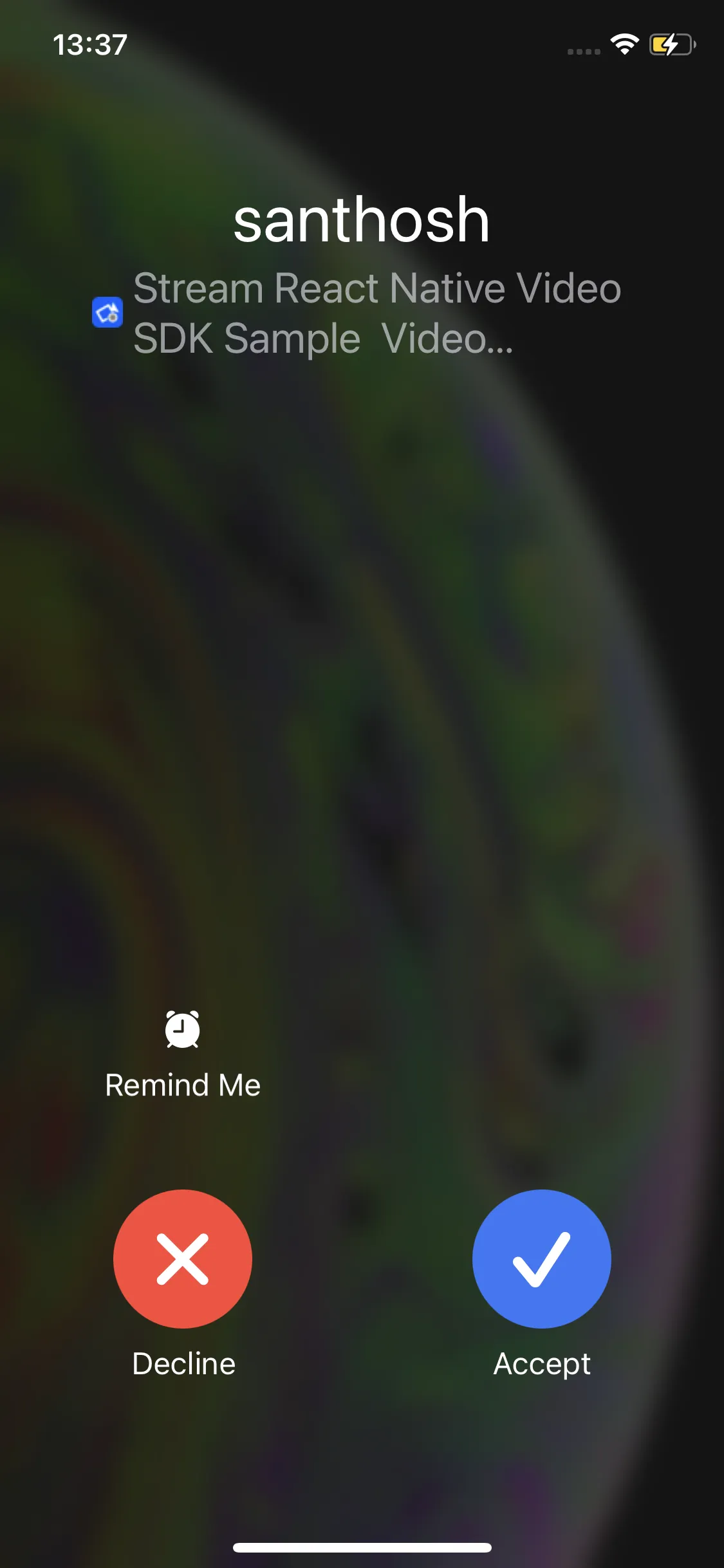 |
Add push provider credentials to Stream
Please follow the below guides for adding appropriate push providers to Stream:
- Android - Firebase Cloud Messaging
- iOS - Apple Push Notification Service (APNs)
Install Dependencies
So what did we install precisely?
@react-native-firebase/appand@react-native-firebase/messagingfor handling incoming Firebase Cloud Messaging notifications on Android.@notifee/react-native- is used to customize and display push notifications.react-native-voip-push-notificationfor handling incoming PushKit notifications on iOS.react-native-callkeepand@config-plugins/react-native-callkeepfor reporting incoming calls to iOS CallKit.
Add Firebase credentials
To create a Firebase project, go to the Firebase console and click on Add project.
In the console, click the setting icon next to Project overview and open Project settings. Then, under Your apps, click the Android icon to open Add Firebase to your Android app and follow the steps. Make sure that the Android package name you enter is the same as the value of
android.packagefrom your app.json.After registering the app, download the google-services.json file and place it in your project’s root directory.
In app.json, add an
android.googleServicesFilefield with the relative path to the downloaded google-services.json file. If you placed it in the root directory, the path is:
{
"android": {
"googleServicesFile": "./google-services.json"
}
}Similarly, for iOS, in the console, click the setting icon next to Project overview and open Project settings. Then, under Your apps, click the iOS icon to open Add Firebase to your Apple app and follow the steps. Make sure that the Apple bundle ID you enter is the same as the value of
ios.bundleIdentifierfrom your app.json.After registering the app, download the GoogleService-Info.plist file and place it in your project’s root directory.
In app.json, add an
ios.googleServicesFilefield with the relative path to the downloaded GoogleService-Info.plist file. If you placed it in the root directory, the path is:
{
"ios": {
"googleServicesFile": "./GoogleService-Info.plist",
},
}The google-services.json and GoogleService-Info.plist files contain unique and non-secret identifiers of your Firebase project. For more information, see Understand Firebase Projects.
We will not be using firebase for iOS. But it is necessary for the setup for react-native-firebase to have the GoogleService-Info.plist file.
Add the config plugin properties
In app.json, in the plugins field, add the ringingPushNotifications property to the @stream-io/video-react-native-sdk plugin. Also, add the @config-plugins/react-native-callkeep plugin.
{
"plugins": [
[
"@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk",
{
"ringingPushNotifications": {
"disableVideoIos": false,
"includesCallsInRecentsIos": false,
"showWhenLockedAndroid": true
},
"androidKeepCallAlive": true,
}
],
"@config-plugins/react-native-callkeep",
[
"@config-plugins/react-native-webrtc",
{
"cameraPermission": "$(PRODUCT_NAME) requires camera access in order to capture and transmit video",
"microphonePermission": "$(PRODUCT_NAME) requires microphone access in order to capture and transmit audio"
}
],
"@react-native-firebase/app",
[
"expo-build-properties",
{
"ios": {
"useFrameworks": "static"
}
}
]
// your other plugins
]
}- The
disableVideoIosfield is used for apps with audio only calls. Pass true to this property to disable video in iOS CallKit. - The
includesCallsInRecentsIosfield is used to show call history. Pass true to show the history of calls made in the iOS native dialer - The
showWhenLockedAndroidfield is used to display a full-screen notification for the incoming call when the phone is locked. Pass true to enable it. - For iOS only, since
firebase-ios-sdkrequiresuse_frameworksthen you want to configureexpo-build-propertiesby adding"useFrameworks": "static".
The plugin adds a foreground service and the necessary permissions for Android. It shows incoming call notifications and keeps video/audio calls active when the app is in the background.
When uploading the app to the Play Store, declare these permissions in the Play Console and explain their usage, including a link to a video demonstrating the service. This is a one-time requirement. For more information, click here.
The added permissions are:
android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CAMERA- To access camera when app goes to backgroundandroid.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MICROPHONE- To access microphone when app goes to backgroundandroid.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_CONNECTED_DEVICE- To access bluetooth headsets when app goes to backgroundandroid.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_DATA_SYNC- To keep video/audio calls alive when both camera and microphone access permissions were not granted
If Expo EAS build is not used, please do npx expo prebuild --clean to generate the native directories again after adding the config plugins.
Optional: Disable Firebase initialisation on iOS
React Native Firebase Messaging automatically registers the device with APNs to receive remote messages. But since we do not use Firebase on iOS, we can disable it via the firebase.json file that we can newly create:
{
"react-native": {
"messaging_ios_auto_register_for_remote_messages": false
}
}Add Firebase message handlers
To process the incoming push notifications, the SDK provides the utility functions that you must add to your existing or new Firebase notification listeners. Below is the snippet of how to add the firebase listeners:
import messaging from "@react-native-firebase/messaging";
import notifee from "@notifee/react-native";
import {
isFirebaseStreamVideoMessage,
firebaseDataHandler,
onAndroidNotifeeEvent,
isNotifeeStreamVideoEvent,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
export const setFirebaseListeners = () => {
// Set up the background message handler
messaging().setBackgroundMessageHandler(async (msg) => {
if (isFirebaseStreamVideoMessage(msg)) {
await firebaseDataHandler(msg.data);
} else {
// your other background notifications (if any)
}
});
// on press handlers of background notifications
notifee.onBackgroundEvent(async (event) => {
if (isNotifeeStreamVideoEvent(event)) {
await onAndroidNotifeeEvent({ event, isBackground: true });
} else {
// your other background notifications (if any)
}
});
// Optionally: set up the foreground message handler
messaging().onMessage((msg) => {
if (isFirebaseStreamVideoMessage(msg)) {
firebaseDataHandler(msg.data);
} else {
// your other foreground notifications (if any)
}
});
// Optionally: on press handlers of foreground notifications
notifee.onForegroundEvent((event) => {
if (isNotifeeStreamVideoEvent(event)) {
onAndroidNotifeeEvent({ event, isBackground: false });
} else {
// your other foreground notifications (if any)
}
});
};The Firebase message handlers
- The
onMessagehandler should not be added if you do not want notifications to show up when the app is in the foreground. When the app is in foreground, you would automatically see the incoming call screen. - The
isFirebaseStreamVideoMessagemethod is used to check if this push message is a video related message. And only this needs to be processed by the SDK. - The
firebaseDataHandlermethod is the callback to be invoked to process the message. This callback reads the message and uses the@notifee/react-nativelibrary to display push notifications.
The Notifee event handlers
- The
onForegroundEventhandler should not be added if you did not add foreground notifications above. - The
isNotifeeStreamVideoEventmethod is used to check if the event was a video related notifee event. And only this needs to be processed by the SDK. - The
onAndroidNotifeeEventmethod is the callback to be invoked to process the event. This callback reads the event and makes sure that the call is accepted or declined.
If you had disabled the initialization of Firebase on iOS, add the above method only for Android using the Platform-specific extensions for React Native.
For example, say you add the following files in your project:
setFirebaseListeners.android.ts
setFirebaseListeners.tsThe method above must only be added to the file that .android extension. The other file must add the method but do nothing like below:
export const setFirebaseListeners = () => {
// do nothing
};Setup the push notifications configuration for the SDK
The SDK automatically processes the incoming push notifications once the setup above is done if the push notifications configuration has been set using StreamVideoRN.setPushConfig. Below is an example of how this method can be called,
import {
StreamVideoClient,
StreamVideoRN,
} from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
import { AndroidImportance } from "@notifee/react-native";
import AsyncStorage from "@react-native-async-storage/async-storage";
import { STREAM_API_KEY } from "../../constants";
export function setPushConfig() {
StreamVideoRN.setPushConfig({
// pass true to inform the SDK that this is an expo app
isExpo: true,
ios: {
// add your push_provider_name for iOS that you have setup in Stream dashboard
pushProviderName: __DEV__ ? "apn-video-staging" : "apn-video-production",
},
android: {
// add your push_provider_name for Android that you have setup in Stream dashboard
pushProviderName: __DEV__
? "firebase-video-staging"
: "firebase-video-production",
// configure the notification channel to be used for incoming calls for Android.
incomingCallChannel: {
id: "stream_incoming_call",
name: "Incoming call notifications",
// This is the advised importance of receiving incoming call notifications.
// This will ensure that the notification will appear on-top-of applications.
importance: AndroidImportance.HIGH,
// optional: if you dont pass a sound, default ringtone will be used
// sound: <your sound url>
},
// configure the functions to create the texts shown in the notification
// for incoming calls in Android.
incomingCallNotificationTextGetters: {
getTitle: (createdUserName: string) =>
`Incoming call from ${createdUserName}`,
getBody: (_createdUserName: string) => "Tap to answer the call",
},
},
// add the async callback to create a video client
// for incoming calls in the background on a push notification
createStreamVideoClient: async () => {
// note that since the method is async,
// you can call your server to get the user data or token or retrieve from offline storage.
const userId = await AsyncStorage.getItem("@userId");
const userName = await AsyncStorage.getItem("@userName");
if (!userId) return undefined;
// an example promise to fetch token from your server
const tokenProvider = () =>
yourServer.getTokenForUser(userId).then((auth) => auth.token);
const user = { id: userId, name: userName };
return StreamVideoClient.getOrCreateInstance({
apiKey: STREAM_API_KEY, // pass your stream api key
user,
tokenProvider,
});
},
});
}Call the created methods outside of the application lifecycle
Call the methods we have created outside of your application cycle. That is inside index.js or the equivalent entry point file. This is because the app can be opened from a dead state through a push notification and in that case, we need to use the configuration and notification callbacks as soon as the JS bridge is initialized.
Following is an example,
import "expo-router/entry";
import { setPushConfig } from "src/utils/setPushConfig";
import { setFirebaseListeners } from "src/utils/setFirebaseListeners";
// Set push config
setPushConfig();
// Set the firebase listeners
setFirebaseListeners();Request for notification permissions in Android
At an appropriate place in your app, request for notification permissions from the user on Android. Below is a small example of how to request permissions in Expo:
import { PermissionsAndroid } from "react-native";
PermissionsAndroid.request(PermissionsAndroid.PERMISSIONS.POST_NOTIFICATIONS);Disabling push - usually on logout
In some cases you would want to disable push from happening. For example, if user logs out of your app. Or if the user switches. You can disable push like below:
import { StreamVideoRN } from "@stream-io/video-react-native-sdk";
await StreamVideoRN.onPushLogout();Optional: On Android show full-screen incoming call view when phone is locked
Passing true to ringingPushNotifications.showWhenLockedAndroid will add the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT permission to the android app and add the necessary configurations to the MainActivity.
For apps installed on phones running versions Android 13 or lower, the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT permission is enabled by default.
For all apps being installed on Android 14 and above, the Google Play Store revokes the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT for apps that do not have calling or alarm functionalities. Which means, while submitting your app to the play store, if you do declare that ‘Making and receiving calls’ is a ‘core’ functionality in your app, this permission is granted by default on Android 14 and above.
If the USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT permission is not granted, the notification will show up as an expanded heads up notification on the lock screen.
Show the incoming and outgoing call UI when app is on the foreground
The last part of the setup for ringing calls is to show the incoming and outgoing call UIs in the app whenever there is a ringing call. If this was not implemented before, please headover to this page of our documentation to implement that.
Troubleshooting
- During development, you may be facing a situation where push notification is shown but its events like accepting or rejecting a call don’t work. This is because, during hot module reloading the global event listeners may get de-registered. To properly test during development, make sure that you fully restart the app or test in release mode without the metro packager.
- You can check the “Webhook & Push Logs” section in the Stream Dashboard to see if Notifications were sent by Stream.
- If you are still having trouble with Push Notifications, please submit a ticket to us at support.
Closed notification behavior on Android
On Android, users can set certain OS-level settings, usually revolving around performance and battery optimization, that can prevent notifications from being delivered when the app is in a killed state. For example, one such setting is the Deep Clear option on OnePlus devices using Android 9 and lower versions.
- Add push provider credentials to Stream
- Install Dependencies
- Add Firebase credentials
- Add the config plugin properties
- Optional: Disable Firebase initialisation on iOS
- Add Firebase message handlers
- Setup the push notifications configuration for the SDK
- Call the created methods outside of the application lifecycle
- Request for notification permissions in Android
- Disabling push - usually on logout
- Optional: On Android show full-screen incoming call view when phone is locked
- Show the incoming and outgoing call UI when app is on the foreground
- Troubleshooting