import 'package:cloud_functions/cloud_functions.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_auth/firebase_auth.dart' as firebase_auth;
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'dart:async';
Future<void> main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
await Firebase.initializeApp();
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Auth(),
),
);
}
}
class Auth extends StatefulWidget {
const Auth({super.key});
@override
_AuthState createState() => _AuthState();
}
class _AuthState extends State<Auth> {
late firebase_auth.FirebaseAuth auth;
late FirebaseFunctions functions;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
auth = firebase_auth.FirebaseAuth.instance;
functions = FirebaseFunctions.instance;
}
final email = 'test@getstream.io';
final password = 'password';
Future<void> createAccount() async {
// Create Firebase account
await auth.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(email: email, password: password);
print('Firebase account created');
}
Future<void> signIn() async {
// Sign in with Firebase
await auth.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email: email, password: password);
print('Firebase signed in');
}
Future<void> signOut() async {
// Revoke Stream chat token.
final callable = functions.httpsCallable('revokeStreamUserToken');
await callable();
print('Stream user token revoked');
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
AuthenticationState(
streamUser: auth.authStateChanges().map(
(firebaseUser) => firebaseUser != null
? User(
id: firebaseUser.uid,
// Map other user fields here
)
: null,
),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: createAccount,
child: const Text('Create account'),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: signIn,
child: const Text('Sign in'),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: signOut,
child: const Text('Sign out'),
),
],
),
);
}
}
class AuthenticationState extends StatelessWidget {
const AuthenticationState({
super.key,
required this.streamUser,
});
final Stream<User?> streamUser;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return StreamBuilder<User?>(
stream: streamUser,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasData) {
return (snapshot.data != null)
? const Text('Authenticated')
: const Text('Not Authenticated');
}
return const Text('Not Authenticated');
},
);
}
}Authentication
Securely generate Stream Chat user tokens using Firebase Authentication and Cloud Functions.
This guide assumes that you are familiar with Firebase Authentication and Cloud Functions for Flutter and using the Flutter Stream Chat SDK.
Introduction
In this guide, you'll explore how you can use Firebase Auth as an authentication provider and create Firebase Cloud functions to securely generate Stream Chat user tokens.
You will use Stream's NodeJS client for Stream account creation and token generation, and Flutter Cloud Functions for Firebase to invoke the cloud functions from your Flutter app.
Stream supports several different backend clients to integrate with your server. This guide only shows an easy way to integrate Stream Chat authentication using Firebase and Flutter.
Flutter Firebase
See the Flutter Firebase getting started docs for setup and installation instructions.
You will also need to add the Flutter Firebase Authentication, and Flutter Firebase Cloud Functions packages to your app. Depending on the platform that you target, there may be specific configurations that you need to do.
Starting Code
The following code shows a basic application with FirebaseAuth and FirebaseFunctions.
You will extend this later to execute cloud functions.
Running the above will give this:
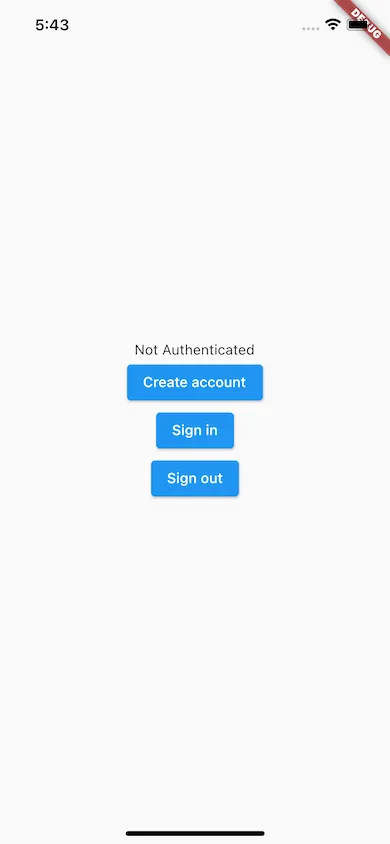
The Auth widget handles all of the authentication logic. It initializes a FirebaseAuth.instance and uses that
in the createAccount, signIn and signOut methods. There is a button to invoke each of these methods.
The FirebaseFunctions.instance will be used later in this guide.
The AuthenticationState`` widget listens toauth.authStateChanges()(mapped to Stream'sUser`)
to display a message indicating if a user is authenticated.
Firebase Cloud Functions
Firebase Cloud Functions allows you to extend Firebase with custom operations that an event can trigger:
- Internal event: For example, when creating a new Firebase account this is automatically triggered.
- External event: For example, directly calling a cloud function from your Flutter application.
To set up your local environment to deploy cloud functions, please see the Cloud Functions getting started docs.
After initializing your project with cloud functions, you should have a functions folder in your project, including a package.json file.
There should be two dependencies already added, firebase-admin and firebase-functions. You will also need to add the stream-chat dependency.
Navigate to the functions folder and run npm install stream-chat --save-prod.
This will install the node module and add it as a dependency to package.json.
Now open index.js and add the following (this is the complete example):
const StreamChat = require("stream-chat").StreamChat;
const functions = require("firebase-functions");
const admin = require("firebase-admin");
admin.initializeApp();
const serverClient = StreamChat.getInstance(
functions.config().stream.key,
functions.config().stream.secret,
);
// When a user is deleted from Firebase their associated Stream account is also deleted.
exports.deleteStreamUser = functions.auth.user().onDelete((user, context) => {
return serverClient.deleteUser(user.uid);
});
// Create a Stream user and return auth token.
exports.createStreamUserAndGetToken = functions.https.onCall(
async (data, context) => {
// Checking that the user is authenticated.
if (!context.auth) {
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"failed-precondition",
"The function must be called " + "while authenticated.",
);
} else {
try {
// Create user using the serverClient.
await serverClient.upsertUser({
id: context.auth.uid,
name: context.auth.token.name,
email: context.auth.token.email,
image: context.auth.token.image,
});
/// Create and return user auth token.
return serverClient.createToken(context.auth.uid);
} catch (err) {
console.error(
`Unable to create user with ID ${context.auth.uid} on Stream. Error ${err}`,
);
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"aborted",
"Could not create Stream user",
);
}
}
},
);
// Get Stream user token.
exports.getStreamUserToken = functions.https.onCall((data, context) => {
// Checking that the user is authenticated.
if (!context.auth) {
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"failed-precondition",
"The function must be called " + "while authenticated.",
);
} else {
try {
return serverClient.createToken(context.auth.uid);
} catch (err) {
console.error(
`Unable to get user token with ID ${context.auth.uid} on Stream. Error ${err}`,
);
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"aborted",
"Could not get Stream user",
);
}
}
});
// Revoke the authenticated user's Stream chat token.
exports.revokeStreamUserToken = functions.https.onCall((data, context) => {
// Checking that the user is authenticated.
if (!context.auth) {
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"failed-precondition",
"The function must be called " + "while authenticated.",
);
} else {
try {
return serverClient.revokeUserToken(context.auth.uid);
} catch (err) {
console.error(
`Unable to revoke user token with ID ${context.auth.uid} on Stream. Error ${err}`,
);
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"aborted",
"Could not get Stream user",
);
}
}
});First, you import the necessary packages and call admin.initializeApp(); to set up Firebase cloud functions.
Next, you initialize the StreamChat server client by calling StreamChat.getInstance. This function requires your Stream app's
token and secret. You can get this from the Stream Dashboard for your app.
Set these values as environment data on Firebase Functions.
firebase functions:config:set stream.key="app-key" stream.secret="app-secret"Replace app-key and app-secret with the values for your Stream app.
This creates an object of stream with properties key and secret. To access this environment
data use functions.config().stream.key and functions.config().stream.secret.
See the Firebase environment configuration documentation for additional information.
To deploy these functions to Firebase, run:
firebase deploy --only functionsCreate a Stream User and Get the User's Token
In the createStreamUserAndGetToken cloud function you create an onCall HTTPS handler, which exposes
a cloud function that can be invoked from your Flutter app.
// Create a Stream user and return auth token.
exports.createStreamUserAndGetToken = functions.https.onCall(
async (data, context) => {
// Checking that the user is authenticated.
if (!context.auth) {
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"failed-precondition",
"The function must be called " + "while authenticated.",
);
} else {
try {
// Create user using the serverClient.
await serverClient.upsertUser({
id: context.auth.uid,
name: context.auth.token.name,
email: context.auth.token.email,
image: context.auth.token.image,
});
/// Create and return user auth token.
return serverClient.createToken(context.auth.uid);
} catch (err) {
console.error(
`Unable to create user with ID ${context.auth.uid} on Stream. Error ${err}`,
);
// Throwing an HttpsError so that the client gets the error details.
throw new functions.https.HttpsError(
"aborted",
"Could not create Stream user",
);
}
}
},
);This function first does a check to see that the client that calls it is authenticated,
by ensuring that context.auth is not null. If it is null, then it throws an HttpsError with a descriptive
message. This error can be caught in your Flutter application.
If the caller is authenticated the function proceeds to use the serverClient to create a new Stream Chat
user by calling the upsertUser method and passing in some user data. It uses the authenticated caller's uid as an id.
After the user is created it generates a token for that user. This token is then returned to the caller.
To call this from Flutter, you will need to use the cloud_functions package.
Update the createAccount method in your Flutter code to the following:
Future<void> createAccount() async {
// Create Firebase account
await auth.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(email: email, password: password);
print('Firebase account created');
// Create Stream user and get token
final callable = functions.httpsCallable('createStreamUserAndGetToken');
final results = await callable();
print('Stream account created, token: ${results.data}');
}Calling this method will do the following:
- Create a new Firebase User and authenticate that user.
- Call the
createStreamUserAndGetTokencloud function and get the Stream user token for the authenticated user.
As you can see, calling a cloud function is easy and will also send all the necessary user authentication information (such as the UID) in the request.
Once you have the Stream user token, you can authenticate your Stream Chat user as you normally would.
Please see our initialization documentation for more information.
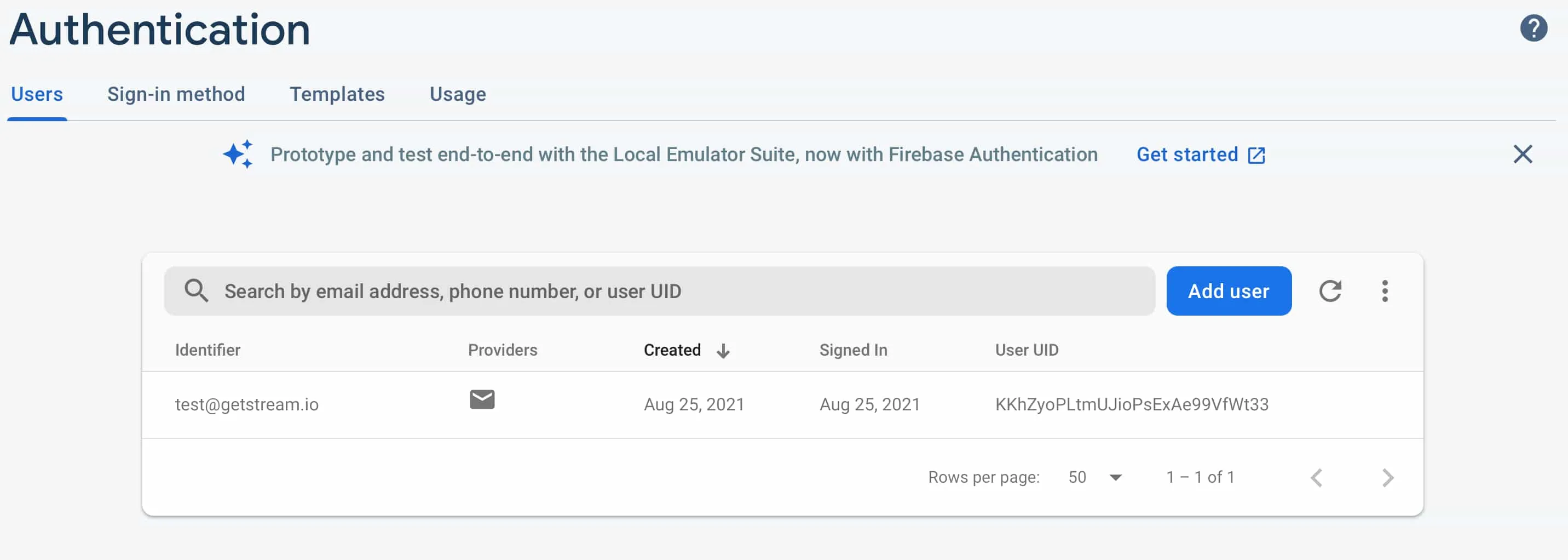
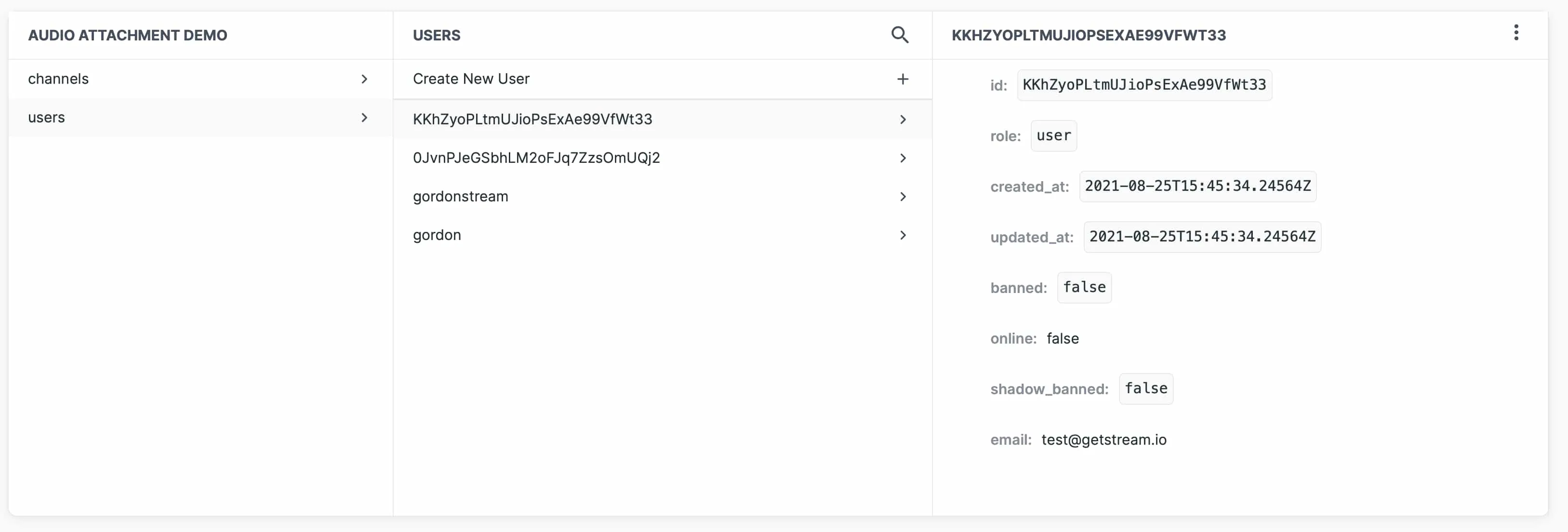
As you can see below, the User ID matches on both Firebase's and Stream's user database.
Firebase Authentication Database
Stream Chat User Database
Get the Stream User Token
The getStreamUserToken cloud function is very similar to the createStreamUserAndGetToken function. The only difference is
that it only creates a user token and does not create a new user account on Stream.
Update the signIn method in your Flutter code to the following:
Future<void> signIn() async {
// Sign in with Firebase
await auth.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email: email, password: password);
print('Firebase signed in');
// Get Stream user token
final callable = functions.httpsCallable('getStreamUserToken');
final results = await callable();
print('Stream user token retrieved: ${results.data}');
}Calling this method will do the following:
- Sign in using Firebase Auth.
- Call the
getStreamUserTokencloud function to get a Stream user token.
The user needs to be authenticated to call this cloud function. Otherwise, the function will throw the failed-precondition error that you specified.
Revoke Stream User Token
You may also want to revoke the Stream user token if you sign out from Firebase.
Update the signOut method in your Flutter code to the following:
Future<void> signOut() async {
// Revoke Stream user token.
final callable = functions.httpsCallable('revokeStreamUserToken');
await callable();
print('Stream user token revoked');
// Sign out Firebase.
await auth.signOut();
print('Firebase signed out');
}Call the cloud function before signing out from Firebase.
Delete Stream User
When deleting a Firebase user account, it would make sense also to delete the associated Stream user account.
The cloud function looks like this:
// When a user is deleted from Firebase their associated Stream account is also deleted.
exports.deleteStreamUser = functions.auth.user().onDelete((user, context) => {
return serverClient.deleteUser(user.uid);
});In this function, you are listening to delete events on Firebase auth. When an account is deleted, this function will be triggered, and you can get the
user's uid and call the deleteUser method on the serverClient.
This is not an external cloud function; it can only be triggered when an account is deleted.
Conclusion
In this guide, you have seen how to securely create Stream Chat tokens using Firebase Authentication and Cloud Functions.
The principles shown in this guide can be applied to your preferred authentication provider and cloud architecture of choice.