const client = StreamChat.getInstance<
AttachmentType,
ChannelType,
CommandType,
EventType,
MessageType,
ReactionType,
UserType
>("YOUR_API_KEY");TypeScript
stream-chat-react-native as well as the client library stream-chat-js are written in TypeScript and therefore provide full TypeScript types and support.
Stream Chat allows for a variety of customizations including custom fields on messages, channels, users, and more. The goal of the Stream Chat TypeScript implementation is to provide static type safety not just on the out of the box Stream Chat implementation, but on custom data provided to the API & SDK as well.
Generics
Generics allow users of the library to accurately represent custom data fields being used by providing typings that are passed to server responses, custom components, filters, etc. In many cases TypeScript can use inference from a provided prop to infer the generics used.
Client
It is important that the proper generics be applied to the stream-chat-js client when it is instantiated.
The documentation on stream-chat-js TypeScript has examples of how this can be done in detail.
The client takes seven optional generics that correspond to the seven customizable fields that currently exist in stream-chat-js.
The seven customizable fields these generics extend are provided via stream-chat-js.
All seven generics contain defaults in the stream-chat-react-native repository that you can extend for custom data.
type DefaultAttachmentType = Record<string, unknown> & {
file_size?: number | string;
mime_type?: string;
};
type DefaultChannelType = Record<string, unknown> & {
image?: string;
};
type DefaultCommandType = string & {};
type DefaultEventType = Record<string, unknown>;
type DefaultMessageType = Record<string, unknown>;
type DefaultReactionType = Record<string, unknown>;
type DefaultUserType = Record<string, unknown> & {
image?: string;
};Additional fields on the defaults that is file_size, mime_type, and image are custom fields used by stream-chat-react-native already within the SDK.
When wanting to set a subset of generics the preceding and interceding generics must also be set in order for the TypeScript compiler to correctly understand intent.
To set ChannelType and MessageType for AttachmentType, CommandType, and EventType must also be set.
const client = StreamChat.getInstance<
DefaultAttachmentType,
{ image?: string; nickName?: string },
DefaultCommandType,
DefaultEventType,
{ isAdminMessage?: boolean }
>("YOUR_API_KEY");DefaultCommandType is set to string & {} instead of string to maintain IntelliSense for the included commands.
In use a string union such as 'poll' | 'question' could be used to extend them.
JSX / TSX
The TypeScript Example App shows how to apply the generics to many of the components in the SDK. Core to understanding this usage is how generics can be applied to JSX elements.
In many cases the use of a single prop such as client or channel allows TypeScript to infer the generics on an element.
In this case LocalAttachmentType is inferred from channel and passed to the props type for a custom Attachment component.
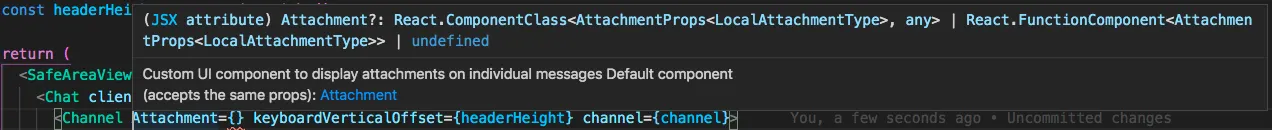
Not all components use or are always provided a prop that can provide inference though.
In these cases the generics must be applied to the component directly.
MessageList for instance could have the previous generics used on client applied to it in a similar manner.
<MessageList<
DefaultAttachmentType,
{ image?: string; nickName?: string },
DefaultCommandType,
DefaultEventType,
{ isAdminMessage?: boolean }
>
onThreadSelect={(thread) => {
/** Set thread and navigate to thread screen */
}}
/>This passes the generics through appropriately to custom components and other props, in this case the custom Message component would receive the generics.
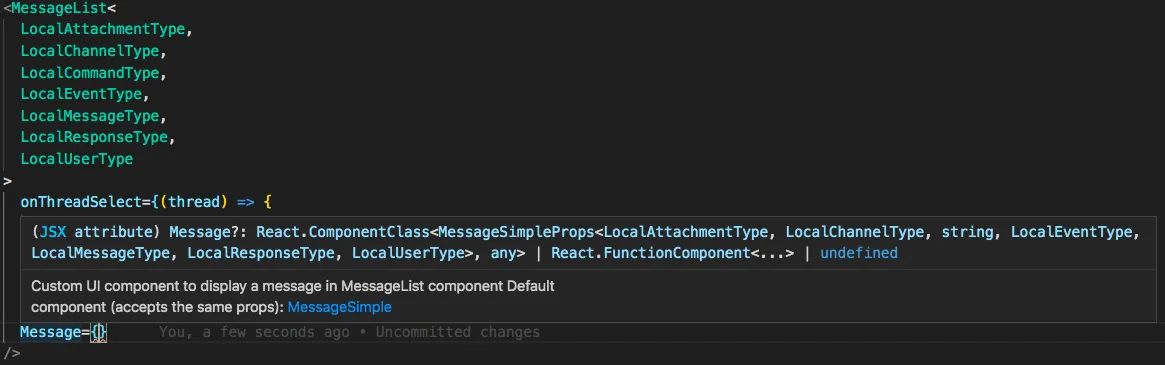
Hooks
Hooks, including those to access contexts, also require generics to be applied to correctly type custom returns.
useChannelContext for instance would have the previous generics applied to it to get a correctly typed return for channel.
const { channel } = useChannelContext<
DefaultAttachmentType,
{ image?: string; nickName?: string },
DefaultCommandType,
DefaultEventType,
{ isAdminMessage?: boolean }
>();Partial inference
Inference only works correctly when all generics are provided by a given input. Partial Type Argument Inference is currently not supported in TypeScript.
Higher Order Components
The lack of partial inference is particularly relevant if Higher Order Components (HOC) are used in place of the provided context hooks.
The withChannelContext HOC accepts the generics similarly to the useChannelContext hook, but because partial inference is not supported the props for the wrapped component must also be explicitly provided.
withChannelContext<
MyComponentProps,
DefaultAttachmentType,
{ image?: string; nickName?: string },
DefaultCommandType,
DefaultEventType,
{ isAdminMessage?: boolean }
>(MyComponent);