call := client.Video().Call("default", uuid.New().String())
// create the call where the WHIP will be sent to
response, err := call.GetOrCreate(ctx, &getstream.GetOrCreateCallRequest{})
// ensure we have a user for the host to send video via WHIP
client.UpdateUsers(ctx, &getstream.UpdateUsersRequest{
Users: map[string]getstream.UserRequest{
"whip-user": {
ID: "whip-user",
},
},
})
// create a token for the user sending video
streamKey, err := client.CreateToken("whip-user-id")
whipURL := response.Data.Call.Ingress.Whip.Address
fmt.Println("WHIP Server URL:", whipURL, "Bearer token:", streamKey)WHIP ingress
You can publish audio and video to any call running on Stream using the WHIP protocol. When using WHIP and OBS, the client will communicate with Stream video edge using webRTC and publish video in multiple layers. The main advantage of WHIP over other ingresses is that encoding happens entirely client-side, this means that publishing via WHIP is free of charge.
Quickstart
Acquire credentials
To get the endpoint and token, you can use the following API:# WHIP URL is: response.call.whip.address
curl -X GET "https://video.stream-io-api.com/api/v2/video/call/livestream/${CALL_ID}?api_key=${API_KEY}" \
-H "Authorization: ${TOKEN}" \
-H "stream-auth-type: jwt"OBS Setup
WHIP adoption is still in its early days, the best way to use WHIP is by downloading the most recent OBS version from Github https://github.com/obsproject/obs-studio/releases
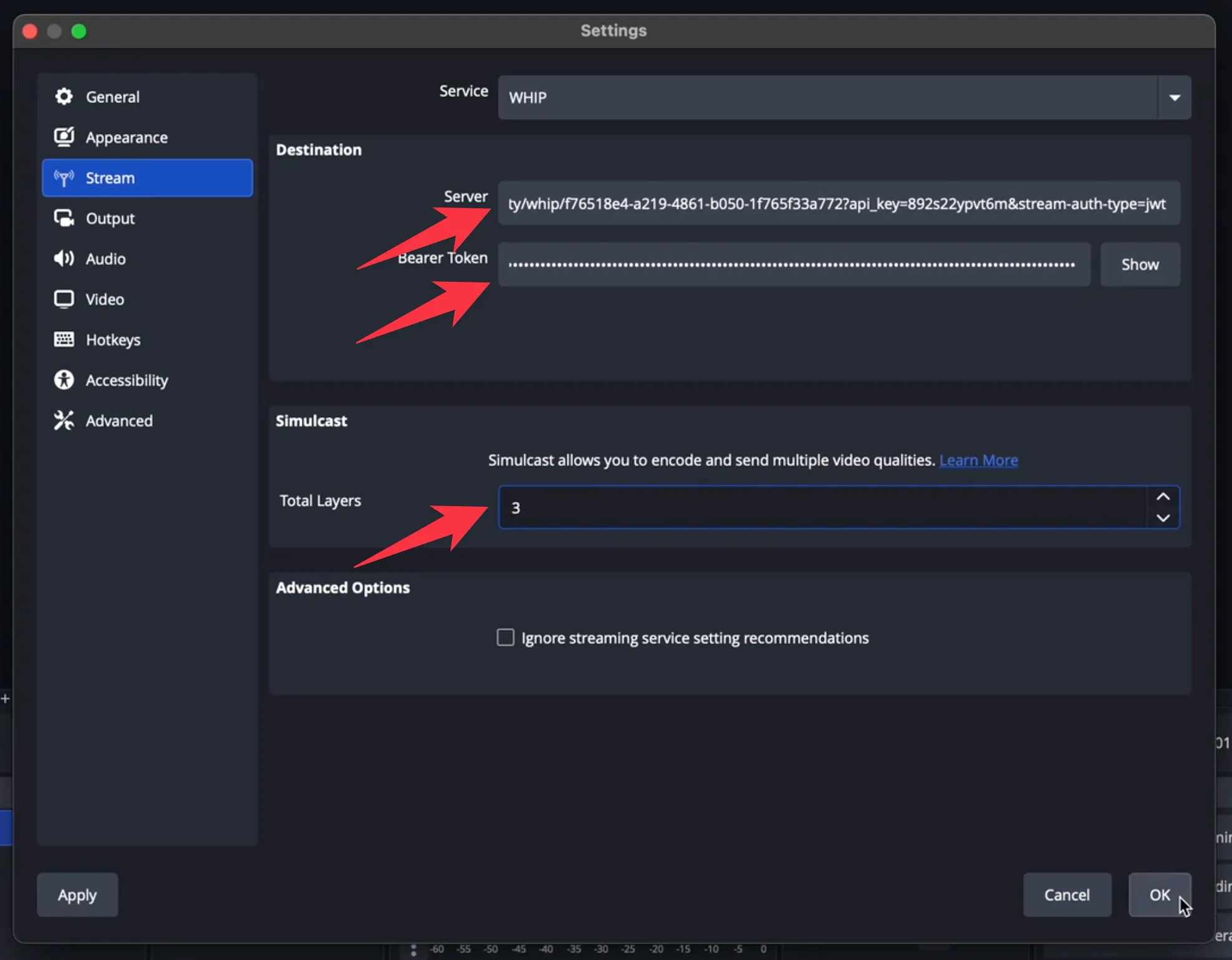
To enable simulcast in OBS:
- Open OBS and go to Settings > Output.
- Select "WHIP" Service.
- Enter Server URL obtained from SDK.
- Enter Bearer token obtained from SDK.
- Set Total Layers to 3. (A maximum of 3 layers are supported.)
The layers represent different video resolutions and bitrates:
- 1 Layer: 100% Height/Width/Bitrate
- 2 Layers:
- 100% Height/Width/Bitrate
- 50% Height/Width/Bitrate
- 3 Layers:
- 100% Height/Width/Bitrate
- 66% Height/Width/Bitrate
- 33% Height/Width/Bitrate
The target resolution and bitrate depend on your content type. See Video bandwidth requirements for detailed guidance.
WHIP vs RTMP and SRT
Stream supports both WHIP, RTMP and SRT here’s a quick comparison to better understand when to use one or the other.
- NO transcoding cost compared to RTMP or SRT input.
- WHIP is a recent protocol, expect adoption on clients and libraries to be more limited.
- H264 support only. (AV1 in beta).
- Better latency compared to RTMP (UDP vs TCP).
- Transcoding happens on the client so increased network and CPU utilisation on client.